Unit 12
The Future of Geospatial Information Technology
The Future of GIS
Sensor Web:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sensor_Web
(cited from Wikipedia) The Sensor Web is a type of sensor network or geographic information system (GIS) that is especially well suited for environmental monitoring and control. In 1997, Kevin Delin of NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory used the term to describe a specific type of sensor network: an amorphous network of spatially distributedsensor platforms (pods) that wirelessly communicate with each other. This amorphous architecture is unique since it is both synchronous and router-free, making it distinct from the more typical TCP/IP-like network schemes. The architecture allows every pod to know what is going on with every other pod throughout the Sensor Web at each measurement cycle.
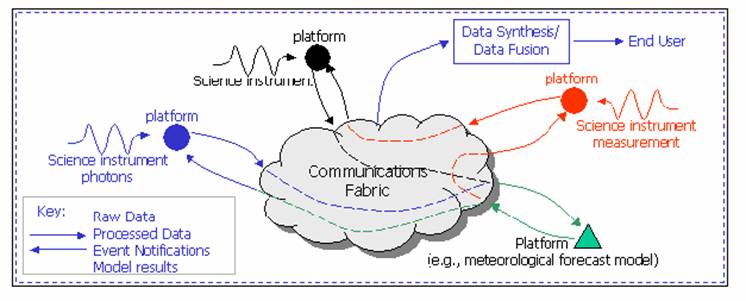
Sensor Web (http://aaaprod.gsfc.nasa.gov/sensorweb/)
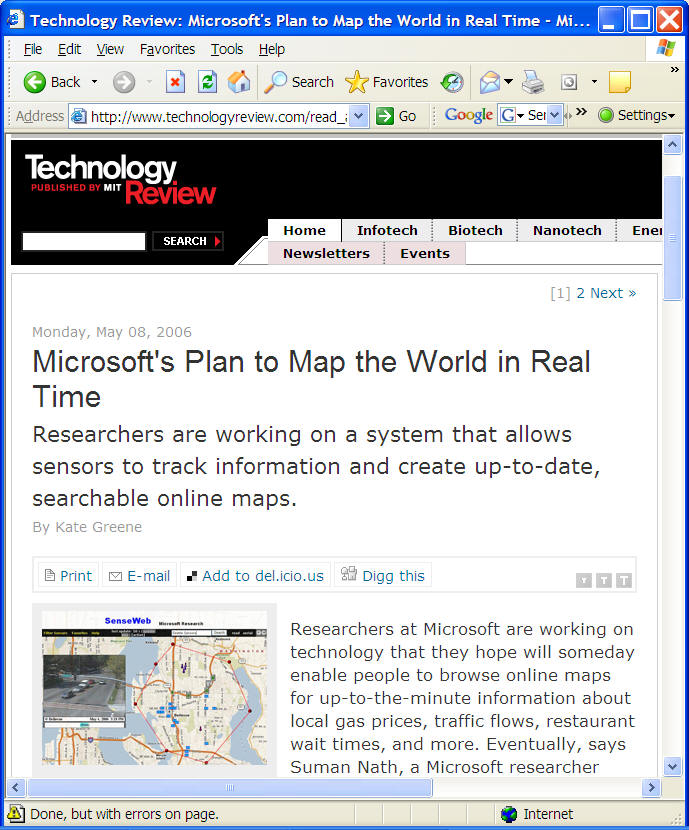
http://www.technologyreview.com/read_article.aspx?id=16781&ch=infotech
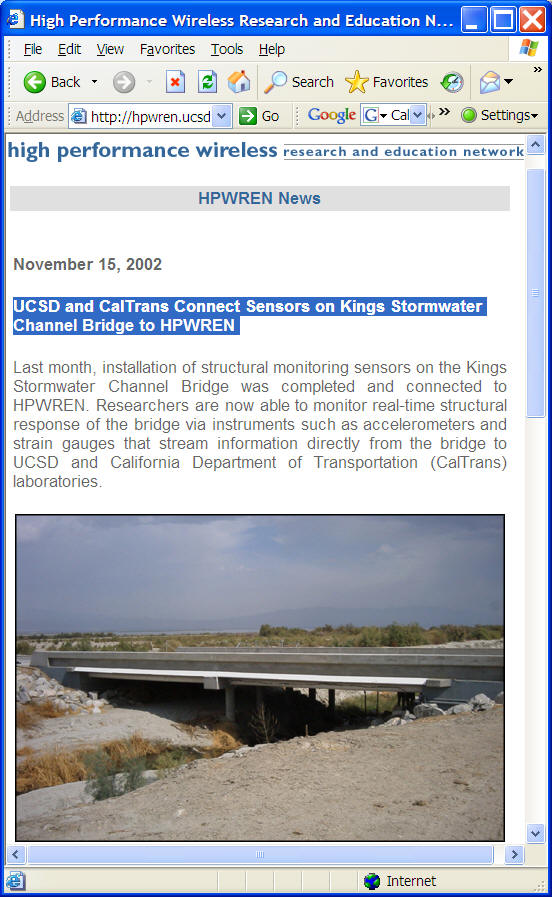
http://hpwren.ucsd.edu/news/021115.html
Air Quality Sensor https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rDTAJmoxeXA
EPA Citizen Science: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lL5tPNn5X48
Smart Vehicle-to-Vehicle communication: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gLXQaU9MuTM
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BXXlodI9gO0
US DoT: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3z09fCqmILU
Machine Learning (Artificial Intelligence) and Deep Learning.
Machine learning is a field of computer science that uses statistical techniques to give computer systems the ability to "learn" (i.e., progressively improve performance on a specific task) with data, without being explicitly programmed.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nKW8Ndu7Mjw (Google)
https://www.coursera.org/learn/machine-learning/lecture/Ujm7v/what-is-machine-learning
Deep learning is the fastest-growing field in machine learning. It uses many-layered Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) to learn levels of representation and abstraction that make sense of data such as images, sound, and text. (cited from https://developer.nvidia.com/deep-learning )
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=b99UVkWzYTQ
What's NEXT? Are we ready for this new AI world? Should we be afraid of these developments?
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Cm_oAaQVWZ8&feature=youtu.be
The Future Directions of GIS
Multiple versions from various institues.
UCGIS 1996 |
|
UCGIS 2004 |
|
David Mark (SUNY-Baffalo)
|
|
GIS textbook (Longley, Goodchild, Rhind) Ten Grand Challenges for GIS |
|
National Research Council (2003). IT Roadmap to a Geospatial Future |
Location-aware Computing; Geospatial Databases and Data Mining; Human Interaction with Geospatial Information; High-quality Geospatial Information. |
[1] UCGIS (via R. McMaster). (1996). Research Priorities for Geographic Information Science. Cartography and Geographic Information Systems, 23 (3), 115-127, 1996.
[2] Mark, D.M. (2000). Geographic Information Science: Critical Issues in an Emerging Cross-Disciplinary Research Domain. Workshop Report, Workshop on Geographic Information Science and Geospatial Activities at NSF. January 14-15, 1999.URISA Journal 12(1): 45 – 54.
[3] National Research Council (2003). IT Roadmap to a Geospatial Future. National Academies Press., Washington, DC. (Available athttp://www.nap.edu/catalog/10661.html)
[4] McMaster, R., and User, E. L. (2004). A Research Agenda for Geographic Information Science. Taylor & Francis. http://www.ucgis.org/priorities/research/2006ResearchNextSteps.htm
