
GEOG 581: Cartography Design

![]()
![]()
Session ONE
![]()
Graduate Student Additional Assignment:
Graduate students will have an additional assignment (one short essay for
related cartographic research topics). (Additional 10% ) The short essay should
be double-spaces, 12-point fonts and between 4 - 6 pages. Examples of essay
topics are the following (you can choose your own topics):
1. The history and development of web-based mapping techniques.
2. The differences between geovisualization paradigm and communication paradigm.
3. GIS vs. Cartography: What are the differences between them?
4. Color use for qualitative data.
(Find more topics from the Cartography and Geographic Information Science
Journal).
Due Day: (Same as the Group Project Report Due data: Dec 14 at 3:00pm.)
![]()
Dr. Arthur H. Robinson, a geographer who improved on the venerable Mercator projection for drawing the round Earth on a flat map, has died. He was 89. http://www.nytimes.com/2004/11/15/obituaries/15robinson.html
(The key person in Communication Paradigm)
![]()
Class Schedule Update:
|
13 |
Nov 25 |
Thanksgiving (NO class this week) |
|
NO lab this week |
|
14 |
Nov 30 (Tuesday) (12:30). |
Visual Thinking and Visualization |
MacEachren Ch.8,9,10 |
Free Lab hour.. (No lab) |
|
15 |
Dec 9 |
The future of cartography |
Slocum. Ch. 25. Clarke, 2002. |
Group Project Presentation |
|
|
14 Dec |
13:00 – 15:00 Office hour. |
Due day for Group project Report (15:00). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
UCSB NCGIA Specialist Meeting: http://www.ncgia.ucsb.edu/projects/nga/
![]()
Map Representation II (Functional Approach)
(MacEachren, ch 6, 7)
[Sign-vehicle] -- [Interpretant] -- [Referent]
Sign-Vehicle as Mediator
| Sign Aspects | |
| Apprise : (provide attribute or location information about objects, meanings) | Stimulate: (behavior, action or feeling) |
| designate | prescribe |
| appraise | emotive |
| indicate | connote |
| label | poetic / aesthetic |
| ??? examples: (I-5) | examples: ?? (STOP) |
Referent as Mediator
Example: Three dimensional space-time referents generated from linking a two-D spatial objects (Time series maps)
Phenomenon-representation (P-reps) -- physical worlds... and Concept-representation (C-reps)... hypotheses from the world.
Interpretant as Mediator (shared understanding between cartographer and percipient).
Map symbol design --> from mimetic to arbitrary
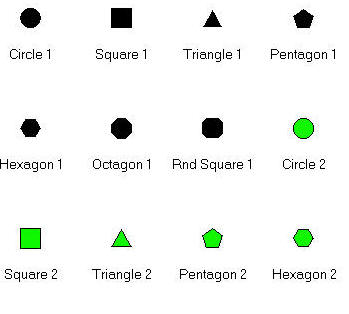
Pictorial symbol, associative symbol, geometric symbols
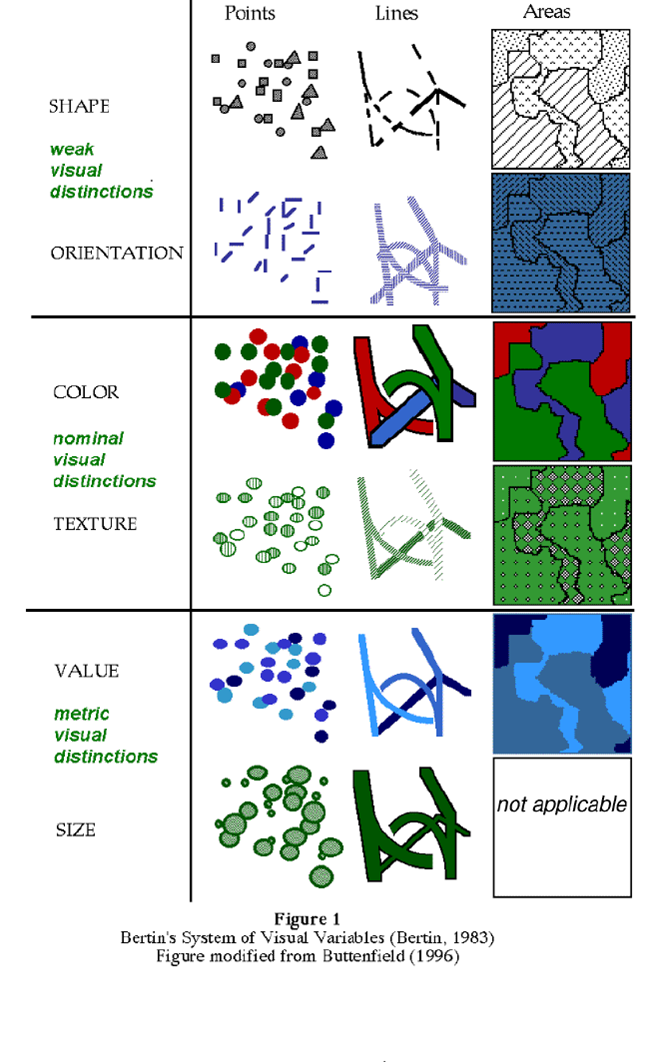
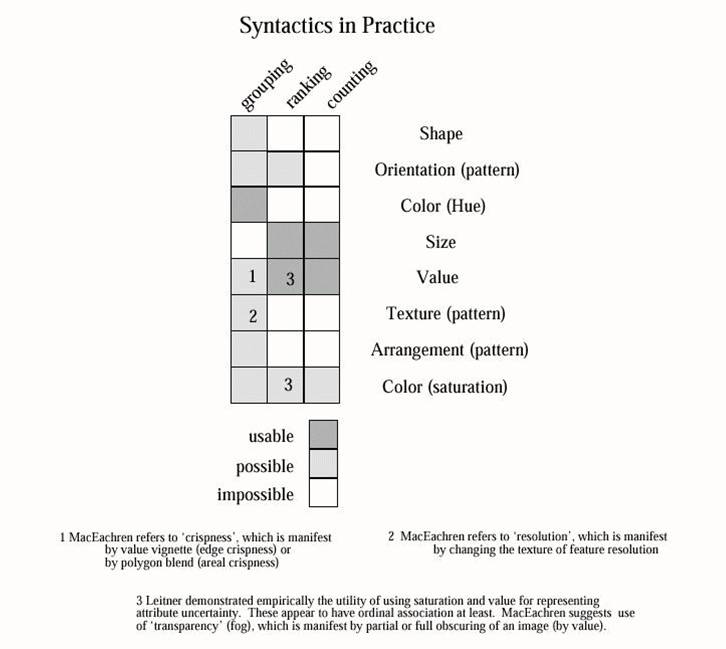
Visual Variables (no complete agreement within cartography)
Page 279.
Static Visual Maps:
(Page.279 for more detail lists).
Dynamic Visual Maps (Animation):
Dynamic Audio Maps
| Location | |
| Loudness | |
| Pitch | |
| Register | |
| Timbre | |
| Duration | |
| Rate of change | |
| Order | |
| Attach/decay |
![]()
Session TWO
![]()
 #1
#1
 #2
#2
 #3
#3
 #4
#4
 #5
#5
 #6
#6
 #7
#7
 #8
#8
 #9
#9
 #10
#10
 #11
#11
 #12
#12
 #13
#13
 #14
#14
 #15
#15
 #16
#16
 #17
#17
 #18
#18
Please use on-line forum to answer the following questions (5 points)
|
What are the differences between "tweened" animation and regular animation in Flash? Which one is better for Web-based animation and WHY? |
|
What are the differences between Java applet animation, Flash animation, and Animated GIF Images? (Use the Web Search for your answers). |
( Java and GIF http://services.valdosta.edu/animation/cool.html )
|
What is "Semantic Web"? What kinds of impacts will this new direction have for the Web-based Mapping and the GIS community? |
![]()
Web-powered by: MAP.SDSU.EDU