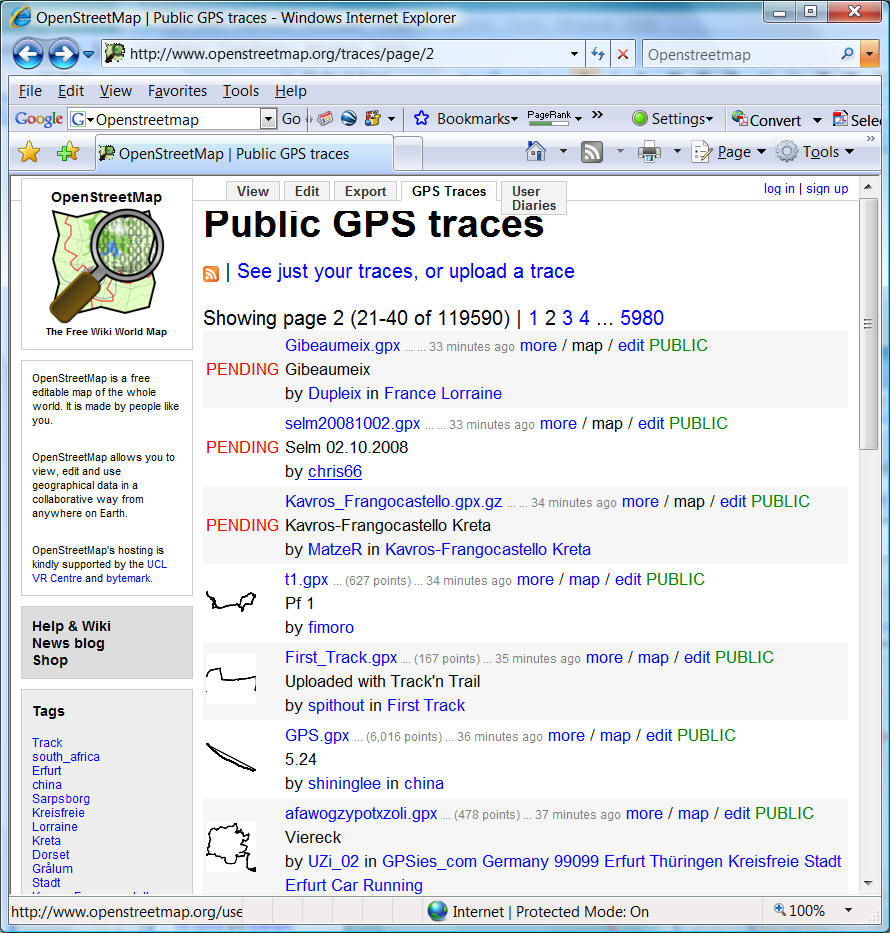
The satellite global
positioning systems are a part of remote sensing domain. It is an
all-weather system offering centimeter positional accuracy. There are two
original satellite positioning systems in the 1990s. One is
the American system called
Global Positioning System (GPS). The other is the Pre-Soviet Union
system called
GLObal NAvigation Satellite System (GLONASS)
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/GLONASS . However, due to the budget
shortage of the Russian satellite global positioning systems, the GLONASS only
have 12 satellites. (need 24 for full functions). Currently, only the USA
GPS system provides complete positioning functions now.
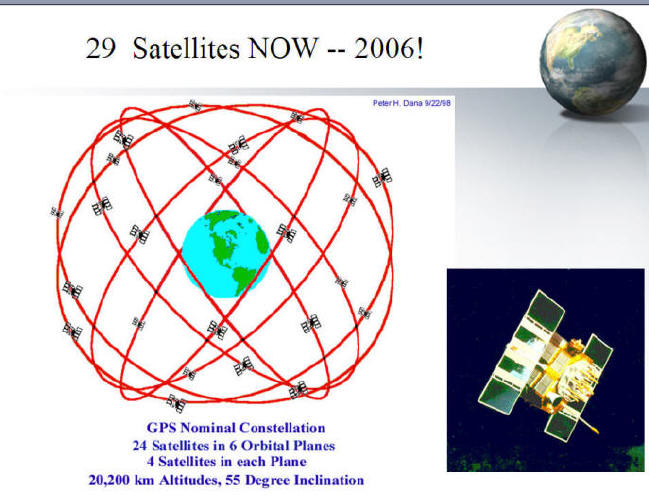
The
GPS satellites: More information:
http://leonardo.jpl.nasa.gov/msl/Programs/gps.html
http://tycho.usno.navy.mil/gpsinfo.html
http://tycho.usno.navy.mil/gpscurr.html (current GPS status)
GPS was
initiated by the U.S. Department of Defense (DOD). In its early
development with the NAVSTAR (Navigation System with Timing And Ranging)
program. GPS was original developed for military use. However, there
have been numerous civil users ever since 1995 when the Full Operational
Capability (FOC) was declared. Common civil applications of GPS technologies can
be categorized into two types: positioning and precise time & frequency
dissemination. Positioning applications include
navigation (aircraft, ships and vehicles), surveying, transportation and
geophysics research. Time accuracy is critical in the telecommunication systems
and electronic power grids. For these areas, some users may find it is useful to
apply GPS to deliver precise time from the atomic clocks for the purpose of time
synchronization
GPS has become a very
powerful tool in field survey and geodesy. There are many different
GPS receivers on the market now. Every type of GPS receivers has its
specific purpose and functions, such as recreational GPS (hiking, biking,
Navigation (cars), GIS and survey (professional), and military use.

The GPS satellites keep sending signals to the Earth. With different time
offsets in receiving the signals, both the three dimensional position and the
GPS time can be obtained. Typically, a user can have five to eight GPS
satellites “visible” at any time.

Before year 2000, the data
accuracy of GPS devices is not consistent because the Selective Availability
(SA) signals which are imposed by the U. S. Air Force. ( Diggelen, 1994 )
The SA signals will reduce the accuracy of ground resolution to 100 meters (
civilian use ) instead of 10 meters ( military use) in 2000. Today with
advanced GPS signal decoding methods, the accuracy of GPS is much better than a
few years ago.

Another problem of GPS comes from the
obstructions issue. When users go down to a deep valley or in a forest, or
in the big city surrounding by the skyscrape, the receiving signals will have
problems and thus reduce the accuracy of observation. Also, if the
receiver can not lock enough satellites, the functions of GPS will become
invalid.
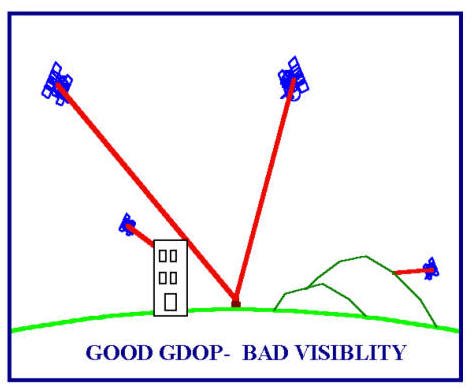
From the
user perspective, the most used equipment is GPS receivers. A minimum of
four satellites
is required to calculate the position, velocity and the GPS time. GPS receivers
can directly process the GPS signals to display the position, speed and time
information for current locations. A Standard Positioning Service
(SPS)
is devised for civil use while there is another Precise Positional
Service
(PPS) for military use. Obviously, SPS provides less accuracy in terms of
positioning and time. To achieve better precision, Differential GPS (DGPS)
technology has been developed. DGPS computes the errors for users with respect
to specific reference stations which are believed to have the same errors as the
users nearby.
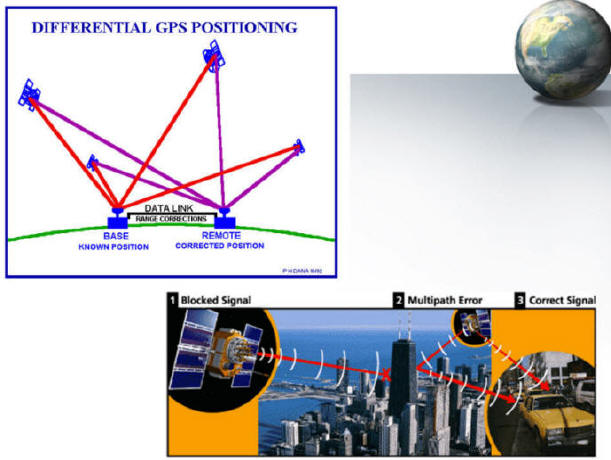
(Note: image source from Peter Dana
http://www.colorado.edu/geography/gcraft/notes/gps/gps_f.html and
Trimble GPS website http://www.trimble.com
)
GPS
receivers can be embedded into mobile phones as well. The so-called GPS mobile
phone has the features of global positioning. GPS is essential for
location-based services. GPS-enable
mobile phones have been widely used in personal navigation, roadside assistance,
and tracking services.
http://client.ecityinteractive.com/sprint/family/demo.html

The E911
(Enhanced 911) mandate has created huge demands for wireless location services.
The trend of future wireless location solutions are towards more accurate, fast,
reliable and less expensive and power consumption services.
SnapTrack’s (http://www.snaptrack.com/)
and NAVIZON (http://www.navizon.com/)
hybrid positioning solutions represent such a trend. Simply using GPS may not
meet the navigation demands of indoors or downtown areas. The combination of
GPS, mobile telecommunication, and Wi-Fi technologies has been proven to be more
cost-effective.
http://www.snaptrack.com/index.jsp
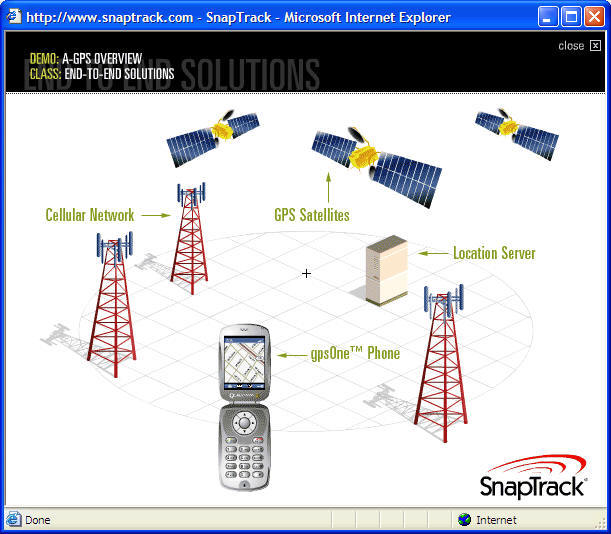
(image from
http://www.snaptrack.com/index.jsp
)
http://www.navizon.com/FullFeatures.htm
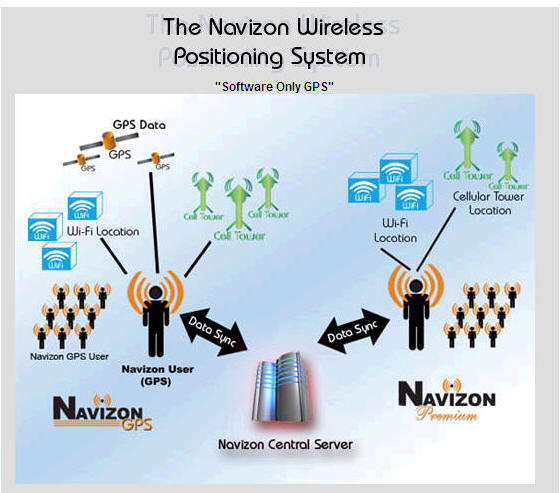
(image
from
http://www.navizon.com/FullFeatures.htm)
The Full
Operational Capability (FOC) of GPS has generated numerous business
opportunities for civil applications. This profitable market encourages the
similar efforts in other counties, such as recent Galieo positioning system by
the European Union.
Galieo
positioning system [1], which is still under deployment, is anticipated to be
functional in 2010. The Galieo positioning system is proposed to have enhanced
features over current GPS technologies such as higher precision, better
reliability and coverage. The major impetus of launching this project is the
concern of European countries of having independent satellite-based positioning
systems.

References:
[1]
WikiPedia.org. The Galileo Positioning System.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Galileo_positioning_system.
A Web-based Satellite Tracking tool
http://www.n2yo.com
Unit 5.2
Location-Based
Services and
GPS Treasure
Hunting Activities
This is a Cool Web Mapping Service ! Find
a nice pub in downtown San Diego...
http://www.unscene.com/
(Nice Web Mapping Design Style and
effects!) -- a good example of
Location-Based Services (LBS).
Definition of LBS: from Wikipedia:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Location-based_service
A location-based service (LBS) is an information and
entertainment service, accessible with mobile devices through
the mobile network and utilizing the ability to
make use of the geographical position
of the mobile device.[1][2][3]
LBS services include services to identify
a location of a person or object, such as discovering the
nearest banking cash machine or the whereabouts of a friend or
employee. LBS services include parcel tracking and vehicle
tracking services. They include personalized weather services
and even location-based games. They are an example of
telecommunication convergence. (source:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Location-based_service)
http://healthmap.org/iphone/

2005
SDSU Geo-Treasure Hunt Event
As Part of our
National GIS Day 2005 activities, SDSU's Geography Department is hosting a
Fast, Fun, Easy, & Free Geo-Treasure Hunt Contest. This Website is
intended to provide you with the most up-to-date and comprehensive information
about the contest and other presentations and activities as part of
National Geography Awareness Week.

Quick Contest Overview
 |
DESCRIPTION:
In a free contest designed with a variety of geospatial technologies such as
GIS. This contest was conceived to highlight geospatial technologies such as
GPSs and GIS. It is also part of the larger
SDSU Geography Week Celebration. |