Geographic Information Science and Spatial Reasoning
(GEOG 104) (A General Education [GE] Course) Spring 2018
|
Geographic Information Science and Spatial Reasoning (GEOG 104) (A General Education [GE] Course) Spring 2018 |
|
| |
| Geographic Information Science and Spatial Reasoning (GEOG 104) (A General Education [GE] Course) Fall 2015 |
Bird-flu Video (8 minutes))
The Second GIS Exercises (ArcGIS Online) . Due day: Sep 29 (Tuesday).
Unit 4.1
GIS Software.
User Interface and User Experiences (UX)
Innovative User Interface Design for Virtual Globles
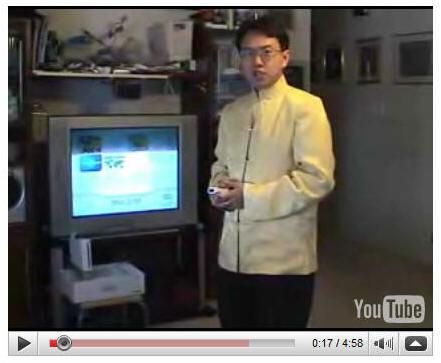
Wii Virtual Globe Demo
A virtual Globe demo in Nintendo Wii by Dr.
Ming-Hsiang Tsou.
YouTube:
http://youtube.com/watch?v=nzRVcCLJOxc
Click here to
download this video!
Innovative Mapping User Interfaces
(demo of Wiimote Whiteboard project)
This project/application was created by Johnny Chung Lee when he was a Ph.D. student in Carnegie Mellon University.
http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~johnny/projects/wii/
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5s5EvhHy7eQ&eurl
How to create an IR Pen?
http://www.kenmooredesign.com/2008/11/how-to-make-infrared-led-light-pen-for.html
Revised whiteboard program for Vista 64 platform: Smoothboard:
http://www.boonjin.com/wp/2008/08/14/wiimote-smoothboard-045-beta
(Excellent revision of the original program. Perfect for Google Earth application)
A very good painting tool: ArtRage (free starter edition): http://www.artrage.com/
(Geographic Information Systems and Sciences Ch 7 8)
Three key parts of GIS software systems: the User Interface, the Tools (Functions), and the Data Manager (Databases).
The User Interface:
Menus, Command Lines
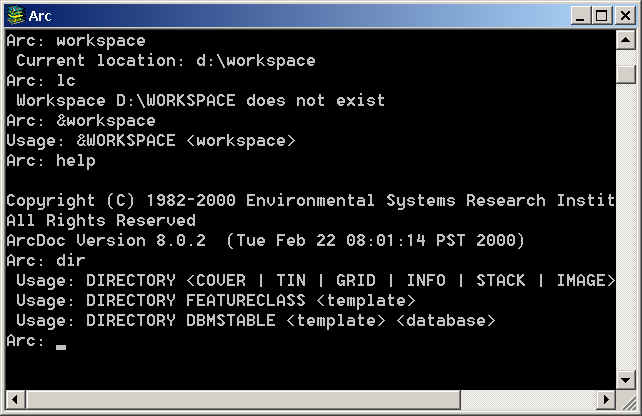
Command Mode: (ARC/INFO workstation)
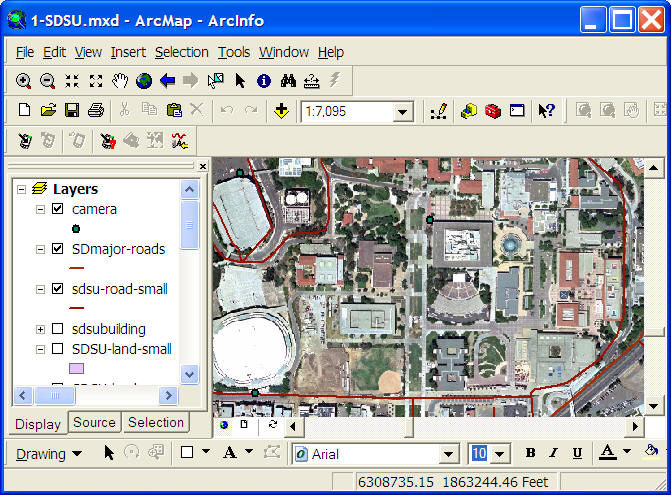
Graphic User Interface (GUIs)
(ArcGIS 9.1 ArcMap Example)
(Show the 2004 ESRI conference move and the 2005 3D Terrain Mapping Table movie)
Question: Have you ever used any computer software? Please tell us your experiences in using these software. (Microsoft Word? Powerpoint? MSN Messenger (Windows Live Messenger ?)
(using Wii FIT scale).http://www.youtube.com/user/SchoeningJohannes
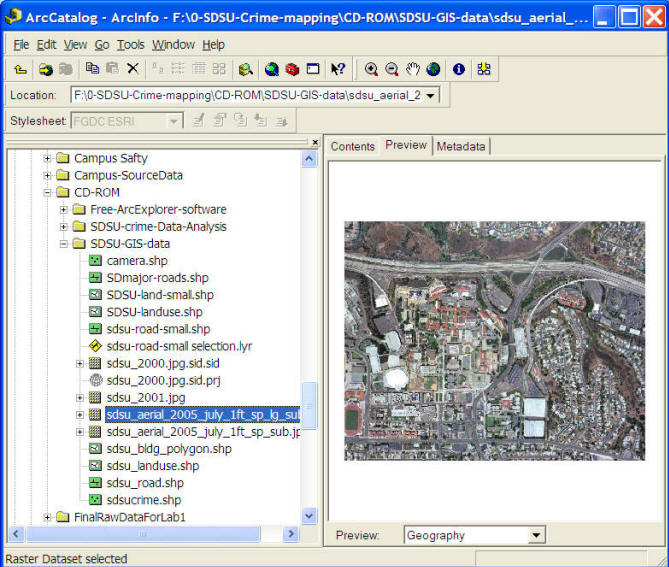
The GIS Tools (functions).
(ArcGIS 9.1 ArcToolbox example)
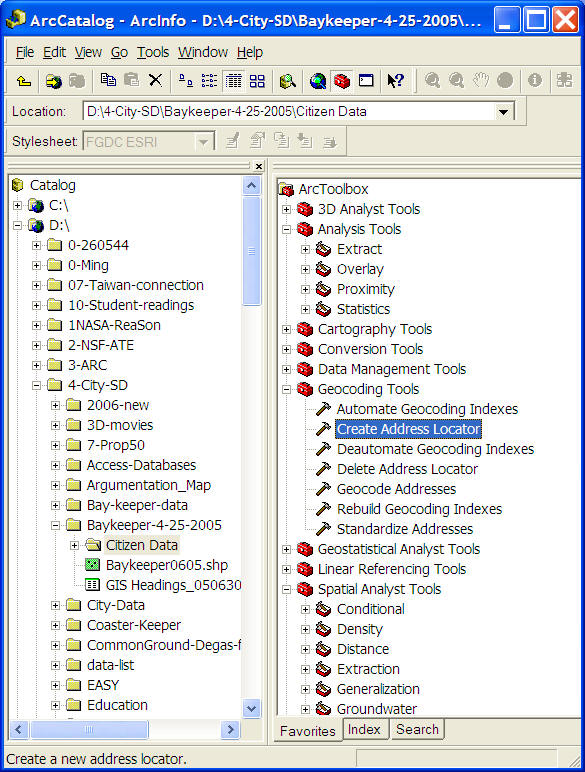
The Data Manager (Databases)
(ArcGIS 9.1-- ArcCatalog).
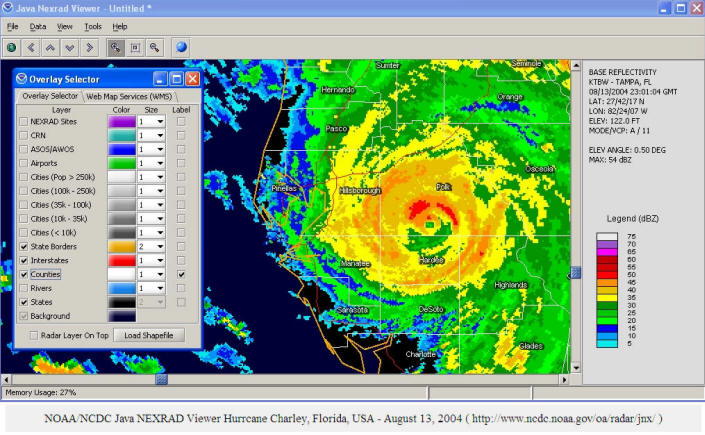
Major functions of GIS software: collecting, storing, managing, querying, analyzing and presenting geographic information (textbook pp158).
Collecting data: Digitizing, Scanning, editing data.
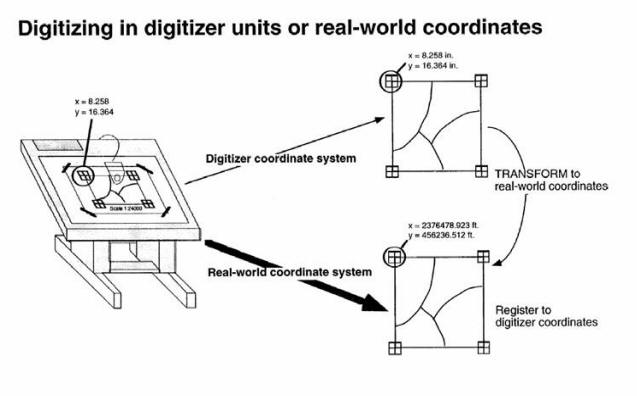
(Image source: ESRI lecture notes).
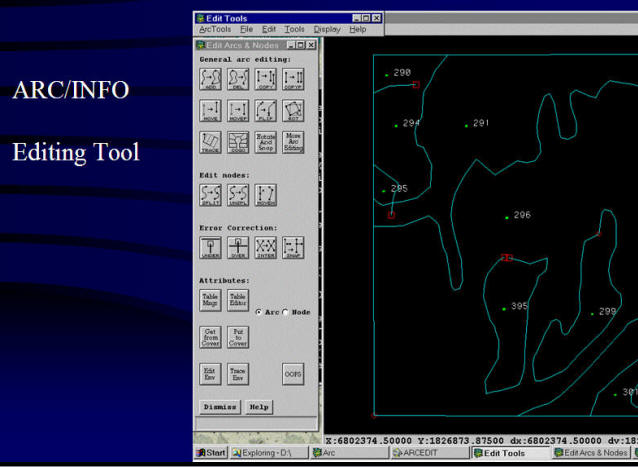

Storing data: (create a data file or a database)
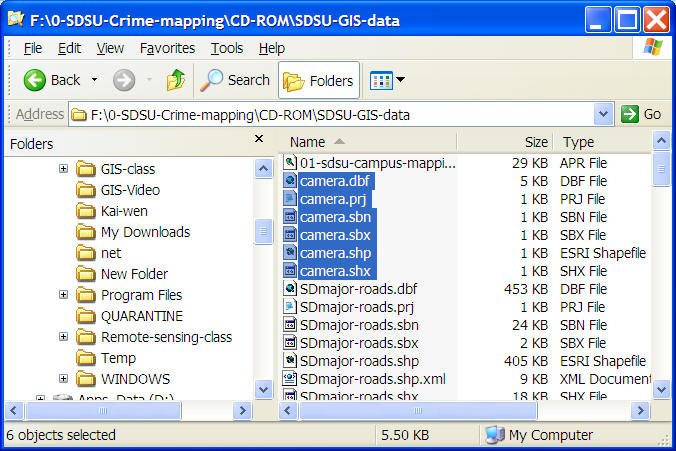
ESRI Shapefiles: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Shapefile
(One data set --> multiple files) .dbf, .prj, .sbn. .sbx .shp .shx
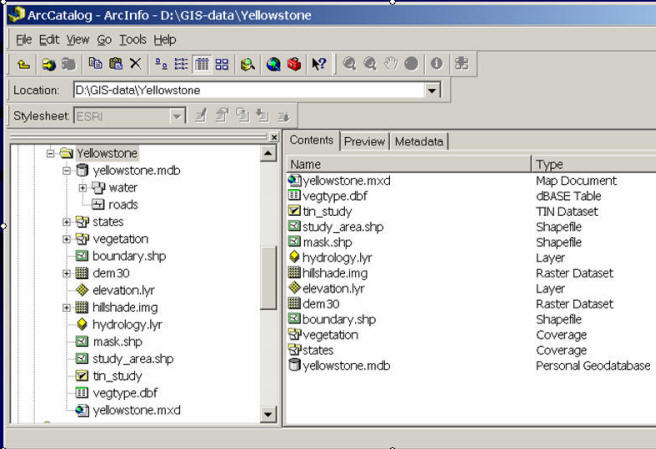
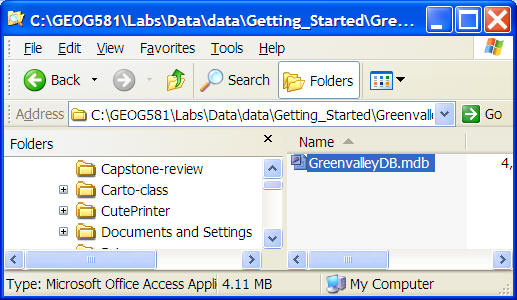
ESRI Personal Geodatabase: (MDB file -- One database --> one file --> multiple data sets)
ESRI: File Geodatabase (File GDB): more powerful with multiple files.
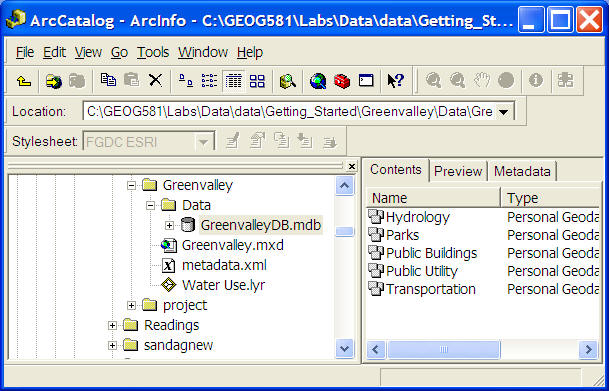
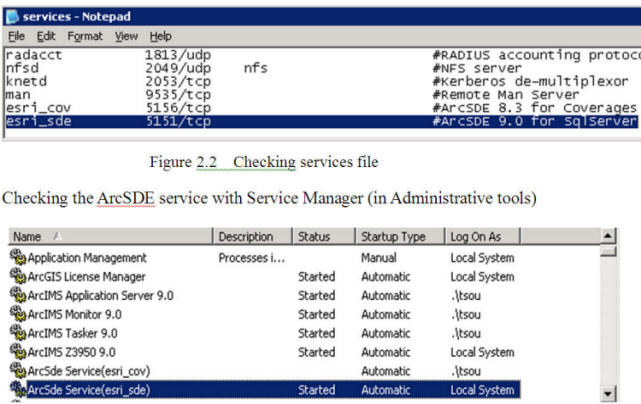
(Middle-ware to link between GIS software and Traditional Databases (MS SQL server, IBM DB2, Oracle Database, etc.)
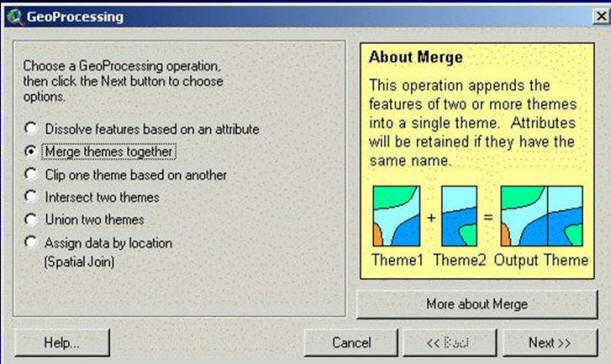
Managing data (update, convert, merge data).
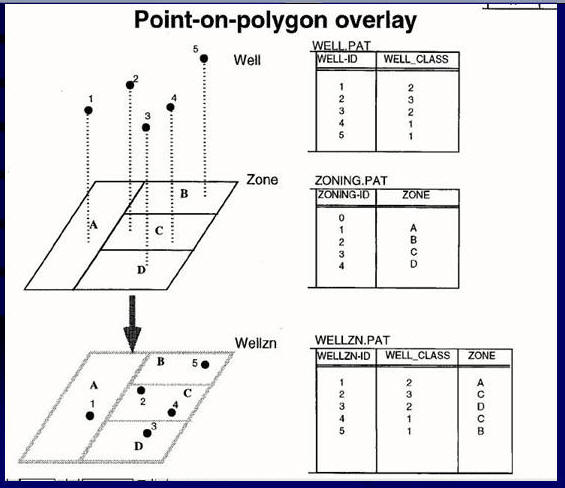
Query data: (Spatial query, attribute query).
Spatial Query Example:

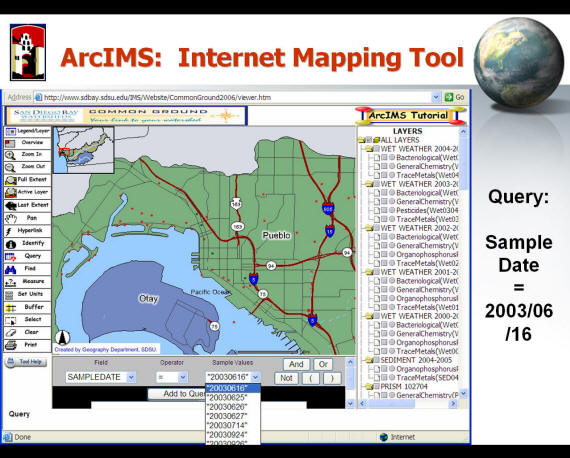
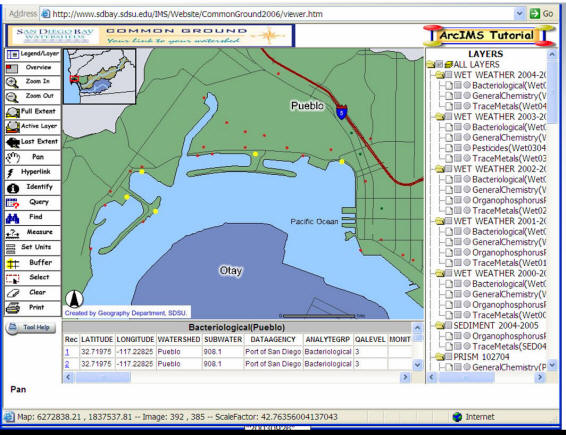
Attribute Query Example:
http://www.sdbay.sdsu.edu (Note: the ArcIMS is no longer available due to the system upgrade.)
GIS Software distribution types:
Commercial products,
ESRI: http://www.esri.com (ArcView, ArcGIS)
Intergraph Inc.: http://www.intergraph.com (GeoMedia, MicroStation)
Autodesk Inc. : http://www.autodesk.com (AutoCAD, MapGuide)
GE Energy (SmallWorld): http://www.gepower.com/prod_serv/index.htm (SmallWorld)
MapInfo: http://www.mapinfo.com/ (MapInfo).


(ESRI Headquarter Office in Redlands)
Shareware, (What is shareware? http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Shareware )
Examples: http://www.agismap.com/
or (ESRI student evaluation version of ArcGIS?) Trail for 60 days).
Public domain software (freeware)
GRASS http://grass.itc.it/index.php
USGS Tools: http://mcmcweb.er.usgs.gov/sdts/public_domain.html
Open source software (freeware)
QGIS: http://www.qgis.org/en/site/ (Open Source Geospatial Foundation: http://www.osgeo.org/ )
GRASS http://grass.itc.it/index.php
Resource: http://opensourcegis.org/
Map Server http://mapserver.gis.umn.edu/
History of GIS Software
|
Decades |
Features |
Milestones |
|
The 1960s |
Operational GIS with loosely coupled computer routines |
The Harvard Laboratory for Computer Graphics and Spatial Analysis, 1965. SYMAP (Synagraphic Mapping System 1966), The Canadian Geographic Information System (CGIS) The establishment of ESRI by Jack Dangermond, 1969 |
|
The 1970s |
GIS with standard user interface and the development of commercial products |
SYMAP POLYVRT and ODYSSEY implemented (computer mapping and analysis packages) |
|
The 1980s |
Development of commercial GIS software; Command line user interactions |
The release of Arc/Info, 1981 MapInfo, founded in 1986 |
|
The 1990s |
Growing GIS markets with several dominating vendors; Graphic User Interfaces; GIS software for specific applications; Customizable software development based on object-oriented programming; Spatial database |
A series of ESRI products (ArcSDE), MapInfo, Intergraph MGE |
|
The 2000s |
Internet GIS with distributed Web Services; GIServices; Interoperability issue; Open source GIS |
Geography network by ESRI; Open GIS Consortium standards widely adopted |
http://makingmaps.wordpress.com/2007/09/12/making-maps-with-a-typewriter/
Examples of SYMAP (The Harvard Laboratory for Computer Graphics and Spatial Analysis)
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5oJIBEvut38 (start at 4:00 in the Youtube video to see the animation).
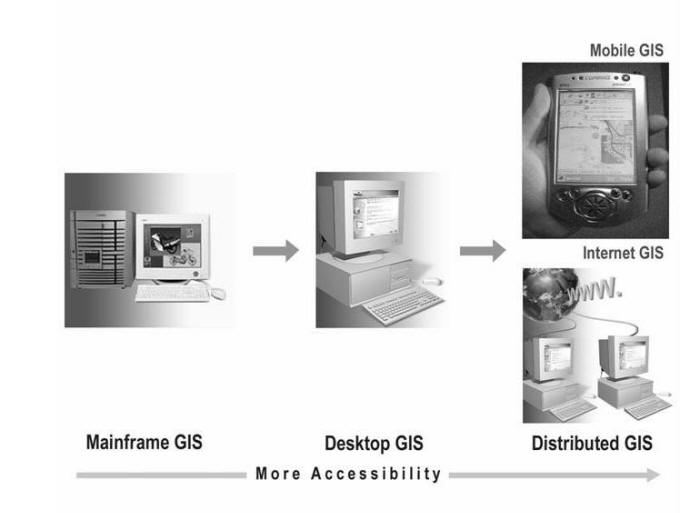
(Image from Peng and Tsou, 2003, Internet GIS).
The Architecture of GIS
Three tiers:
Presentation (user interface),
Business logic (tools - middleware), and
Data server (data management)
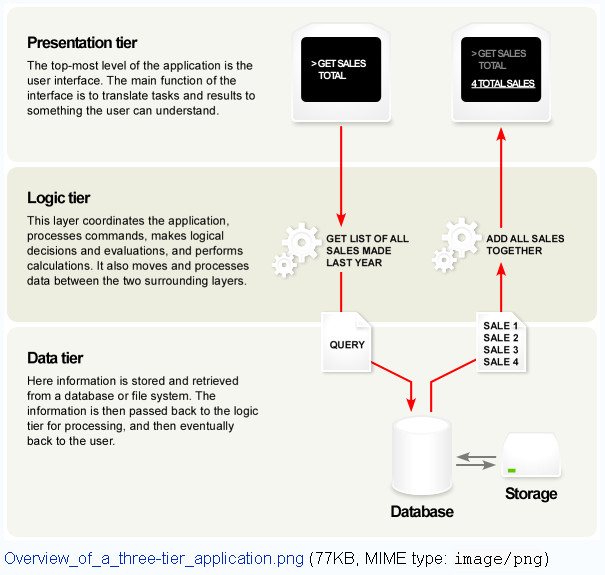
( http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Image:Overview_of_a_three-tier_application.png )
Four types of GISystems:
Desktop GIS

Client-server (C/S),

Centralized severs.
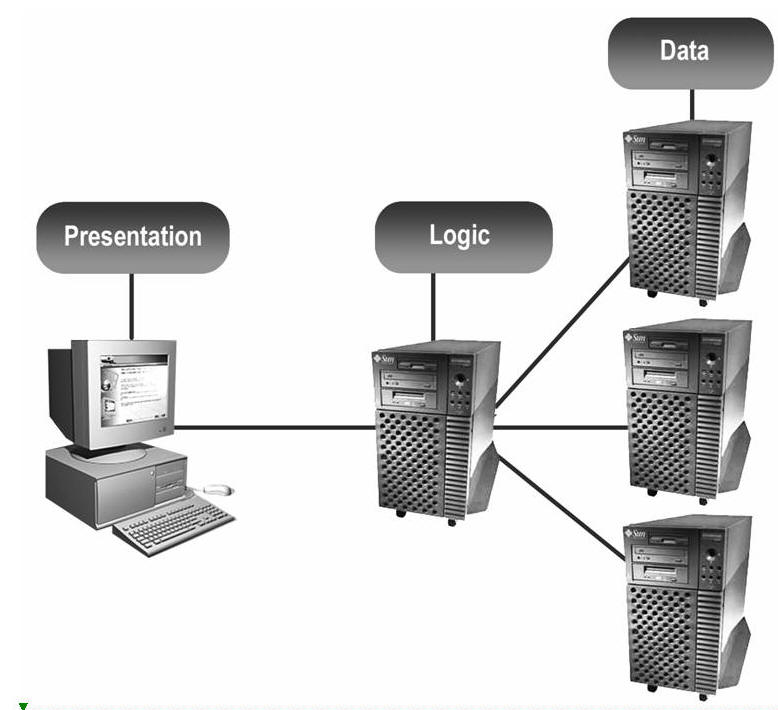
Distributed GIS
GIS Software Customization
Standard programming languages are adopted (Java, C++, Visual Basic, and python).
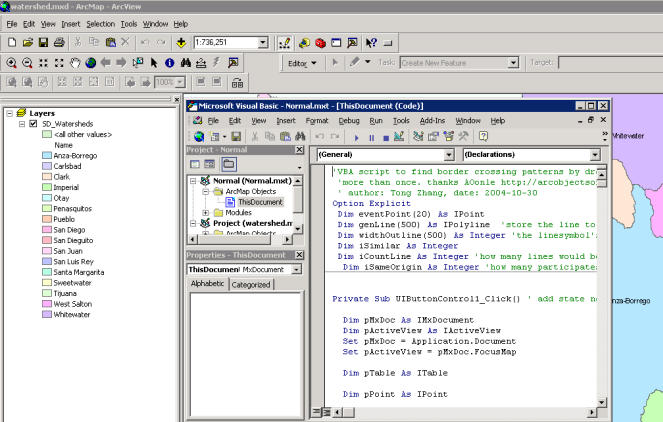
ArcGIS (Visual Basic)
Visual programming with integrated development environments (IDEs).
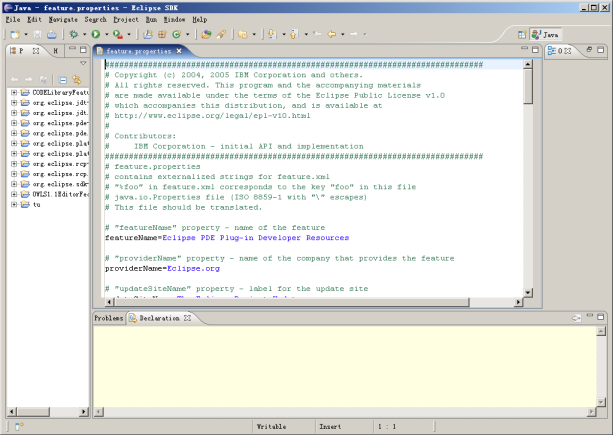
Eclipse (A Java IDE)
API: Application Programming Interfaces.
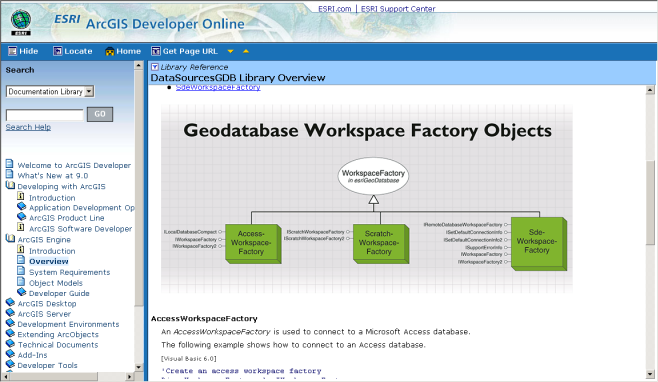
ArcGIS Developer Online (http://edndoc.esri.com/arcobjects/9.0/)
ArcGIS Python http://www.esri.com/news/arcuser/0405/files/python.pdf

ArcGIS Model Builder (Visual Programming / Modeling Tool)
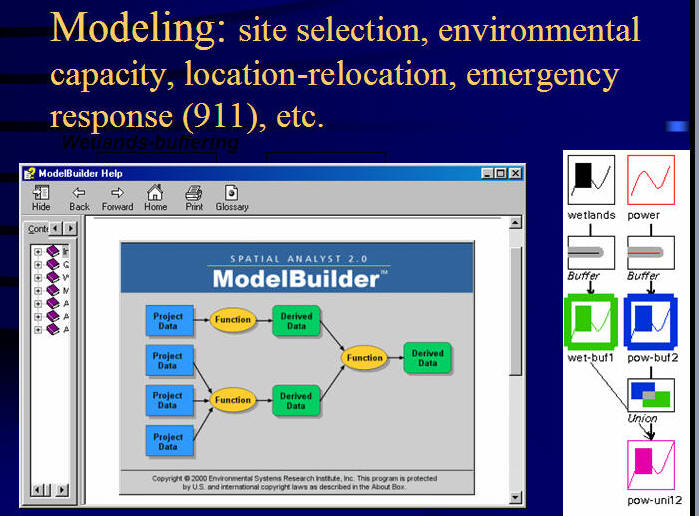
(2004- ESRI conference Epidemiology move.)
Strategies of Building GISystems
Commercial products vs. open source tools .
Geotools: http://geotools.codehaus.org/ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/GeoTools
GeoTools is an open source (LGPL) Java code library which provides standards compliant methods for the manipulation of geospatial data.
PostGIS: http://postgis.refractions.net/
More OpenSource GIS tools: http://opensourcegis.org/
Discuss:
Which types of GIS platforms you prefer? Discuss with costs, training, administration, reliability, scalability, robustness and availability between commercial GIS vs. opensource GIS.
GIS Software Types
Desktop GIS (ArcView, ArcInfo),
Server GIS (ArcGIS Server, ArcIMS -- Internet Map Server),
Developer GIS (Programming Tools, ArcObjects, MapObjects, ArcGIS Engine),
Hand-held GIS (ArcPAD),
GIS Database Middleware and Extensions (ArcSDE, PostGIS),
Unit 4.2
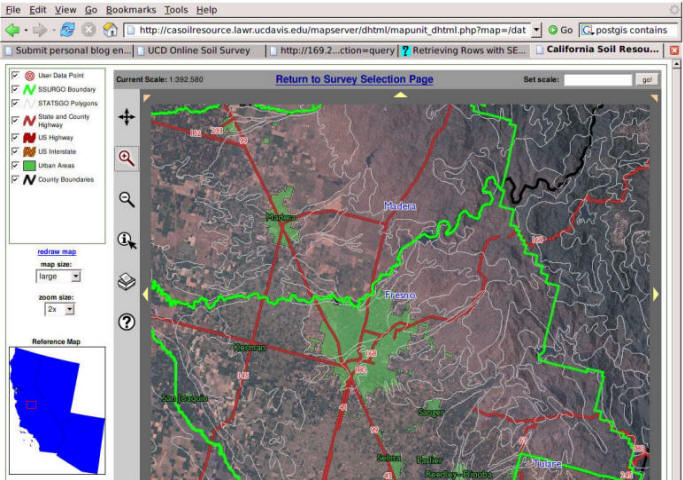
Geographic Data Modeling
The definition of data model:
"A data model is a set of constructs for describing and representing parts of the real world in a digital computer system." (textbook, p. 177).
Why data model is important? Different data model --> different spatial analysis capabilities.
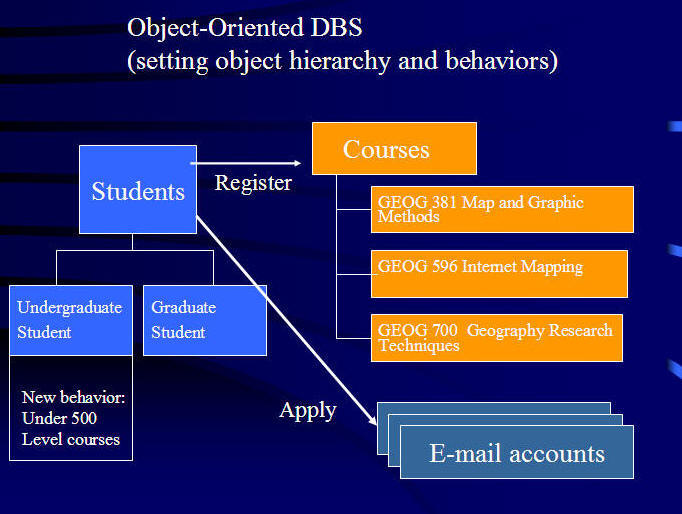
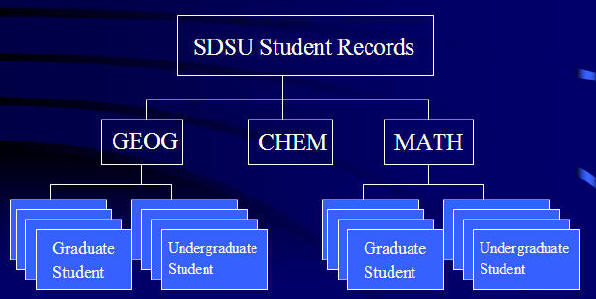
Example of Data model: SDSU Student Information.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Object-oriented_programming
http://www.apl.jhu.edu/~jcstaff/oodev/oointro/models/sld010.htm
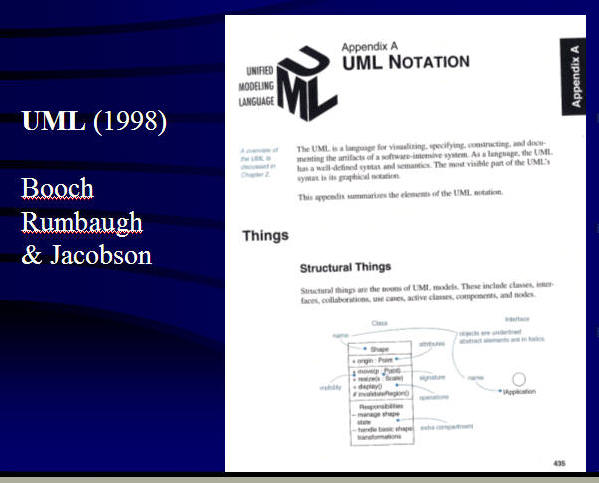
UML and the design of diagrams.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Unified_Modeling_Language
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Class_diagram
Four Levels of Data Model Abstraction : Reality --> Conceptual model --> Logical model --> Physical model.
Real World:

Conceptual Model: Digital Elevation Model (DEM)
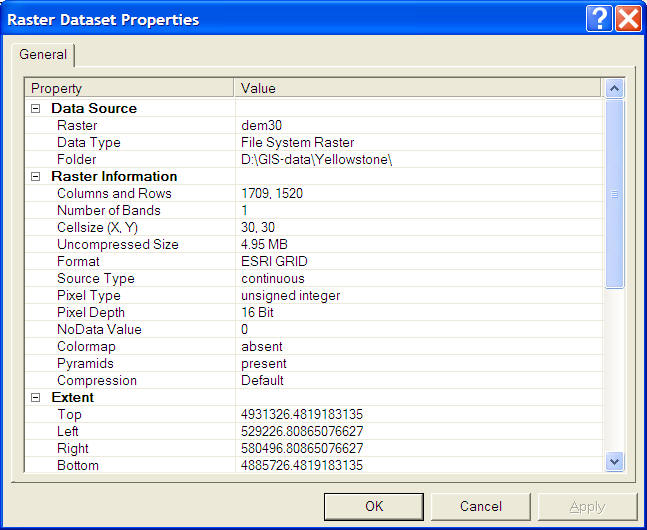
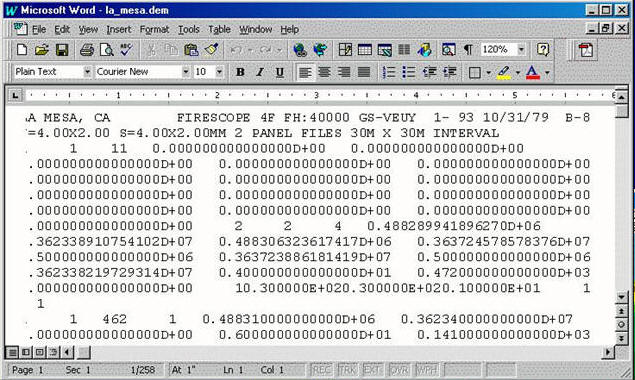
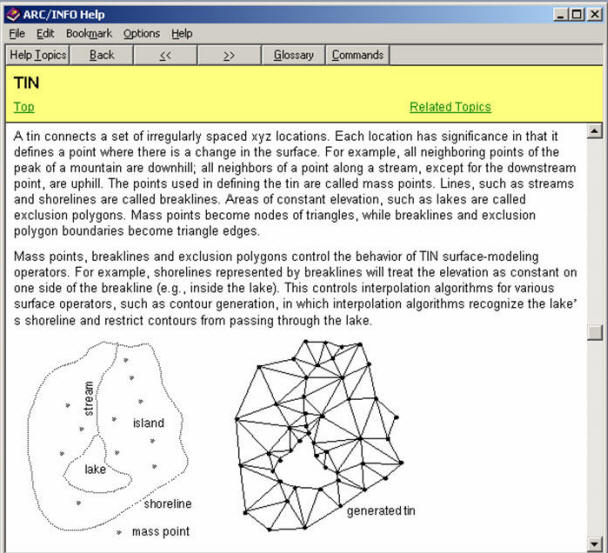
Logical Model: TIN
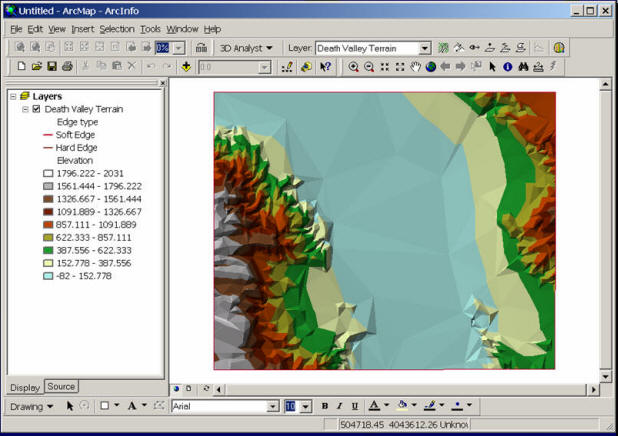
Physical Model (ArcGIS ArcScene).
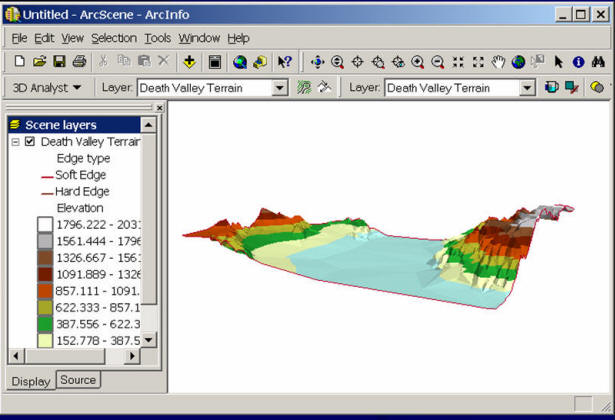
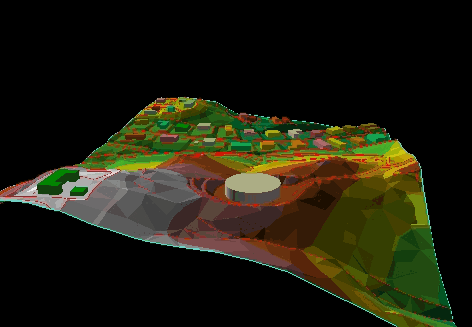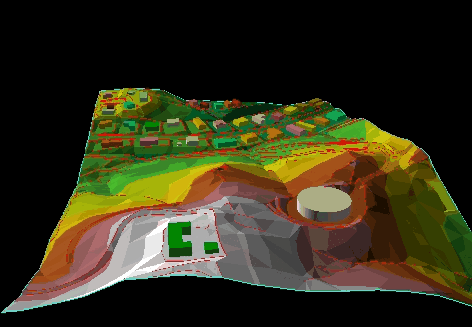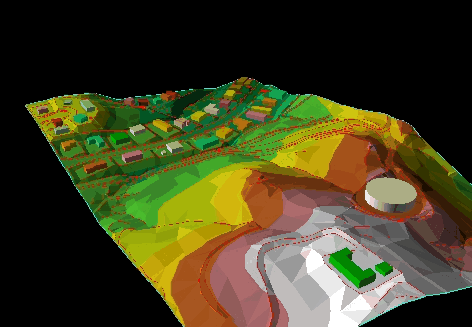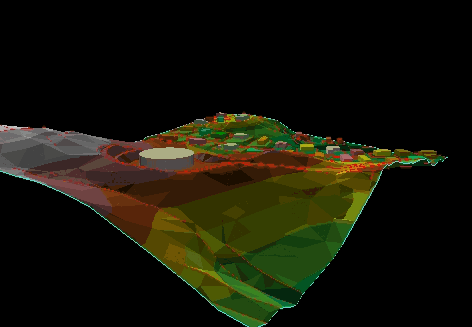
The Comparison between CAD, Graphical, and GIS Data Models
Traditional CAD (Computerized Aid-ed Design and drafting ) Data Model. No Topological relationship. Fast drawing. Good 3D functions.

Graphic Design Tools: (Freehand, Canvas, Painter). (No Databases or Attributes for graphic elements (points, lines, polygons). Purely presentation purpose. No query functions.
GIS Data Model: Connecting Attributes and Graphic elements, include topology relationships. Very large size of data and very complicated drawing procedures (multiple map layers).
Discussion: Why CAD (Computer-aided Design) is not suited for describing geographic information ?
(Coordinates, identification, no topology, Spatial Analysis Function)
[E-Business with GIS] Movie
(Review of Unit-3 Questions....)
GIS Data Format:
A. Raster Data Model and File Compression
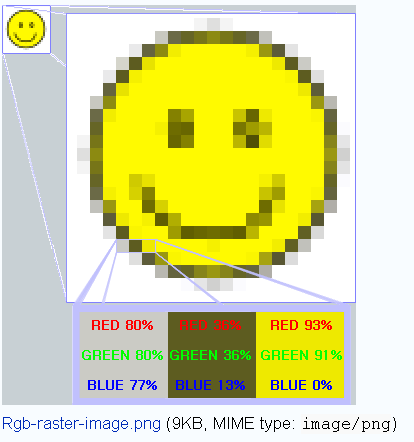
(http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Image:Rgb-raster-image.png)
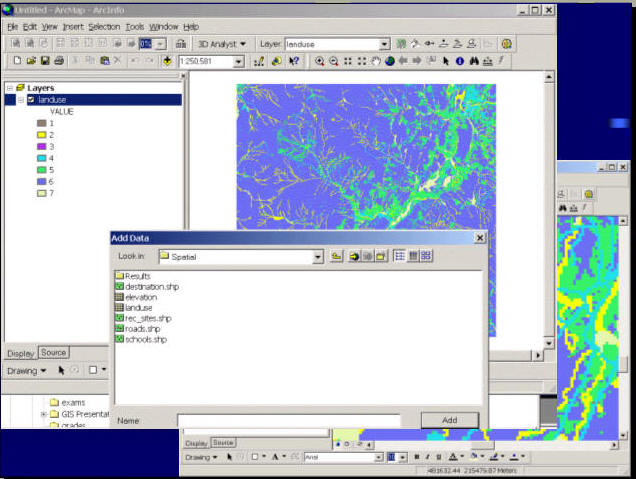
Encoding Method:
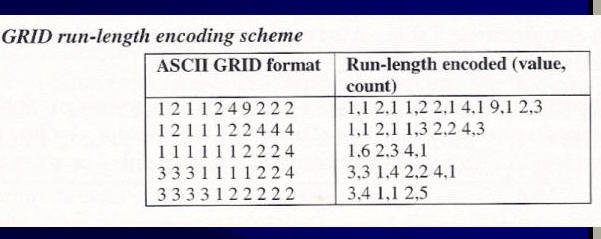
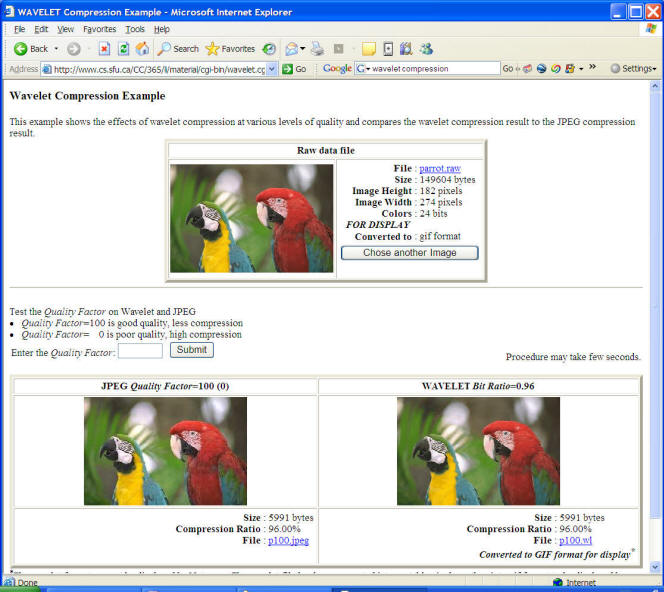
Use compression technologies; wavelet compression techniques (MrSID, ECW)
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wavelet_compression .
http://www.cs.sfu.ca/CC/365/li/material/misc/wavelet.html
Size of Images: How many bands (Layers)? What's the storage size for each pixel? (2 bits?, 8 bits (One byte)? 24 bits (3 bytes)?
(Four Bands -- First-Blue, Second-Green, Three (not used), Four-RED).
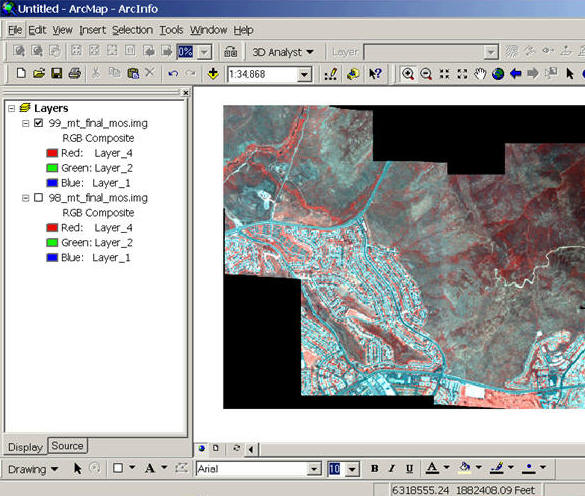
(The size of each pixel)

Images size: 24MB
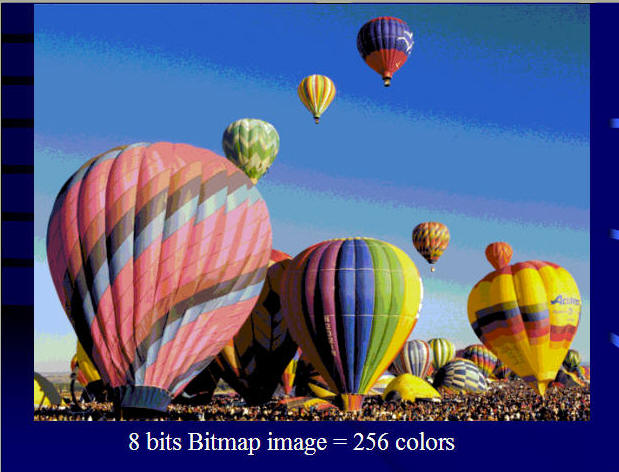

Image size: 8MB

Image size: 4MB
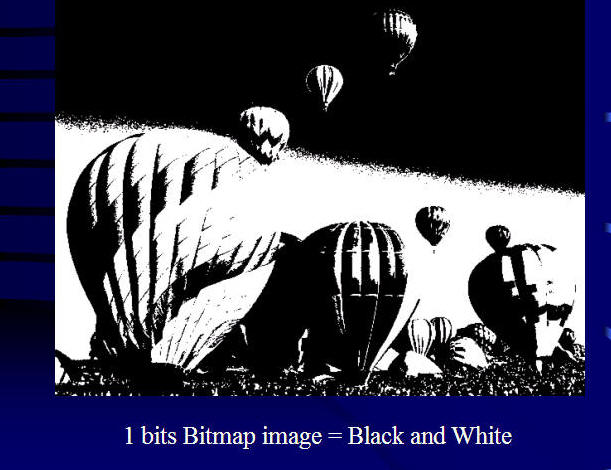

Image size: 1MB
Discussions: What are the advantages and disadvantages of raster data models?
B. Vector Data Model
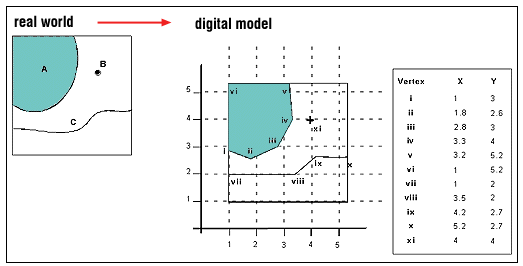
(http://www.sli.unimelb.edu.au/gisweb/GISModule/GIST_Vector.htm)
Vertex: any point on the polygon where two sides (line segments) meet or connect.
Vector model = simple features + topological relations.
Features are vector objects of type point, polyline, or polygon. (p. 184),
Topology is the science and mathematics of relationships used to validate the geometry of vector entities, and for operations such as network tracing and tests of polygon adjacency. (p. 184)
ESRI ARC/INFO Topology
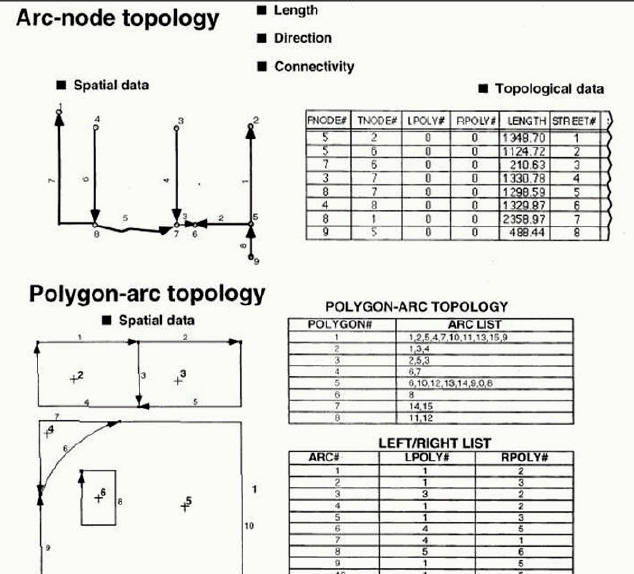
(Image from ESRI lecture notes)
###.AAT (Arc Attribute Table)
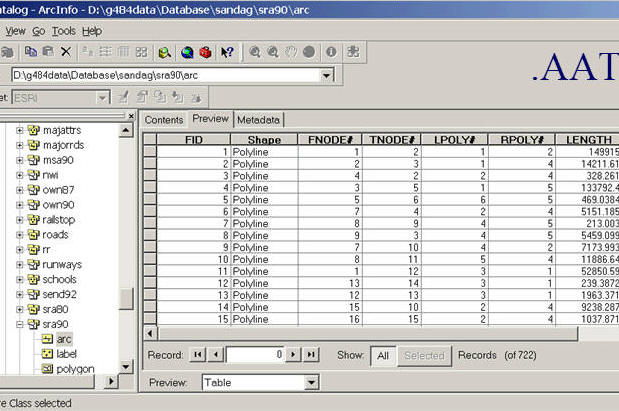

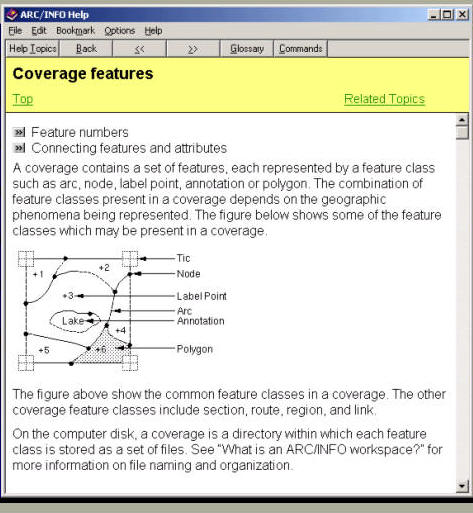
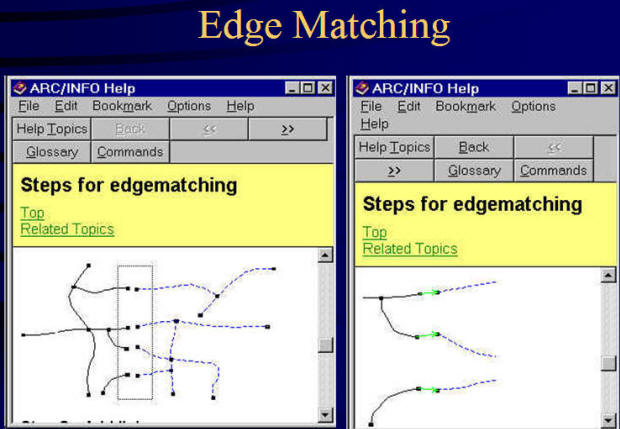
Discussion: Why we need topology? (Data validation, editing, consistency, query efficiency)
Discussions: What are the advantages and disadvantages of vector data models?
(See http://www.innovativegis.com/basis/primer/concepts.html)
TIN Data Model
Triangulated Irregular Networks (TINs)
TIN is used to create, store, analyze and display surface information.
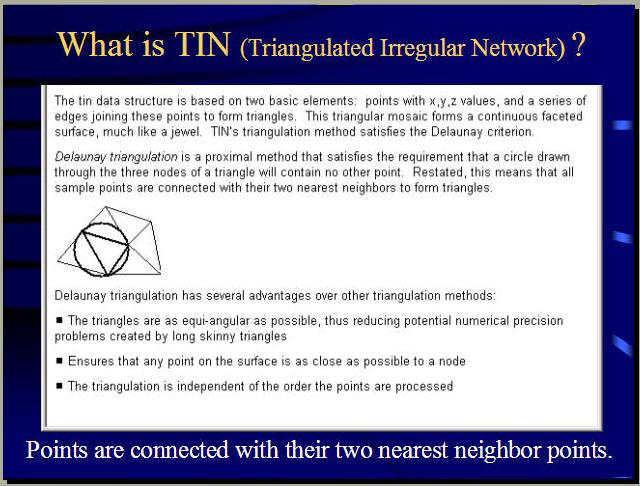
Images from ESRI ARC/INFO help file.
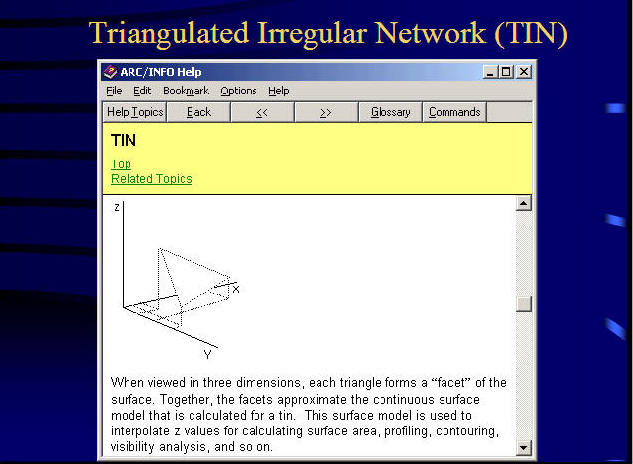
Images from ESRI ARC/INFO help file.

Images from ESRI ARC/INFO help file.
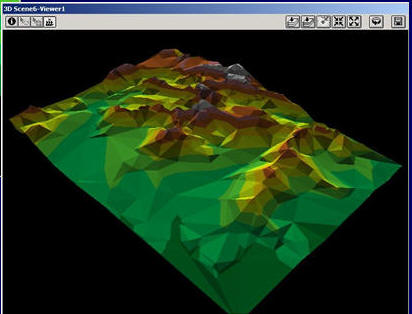
TIN Data Model Advantages:
l Compact Data format (save disk space).
l Consisting of irregular nodes and lines;
l Accurately describing the relief;
l Topological vector structure;
l Flexible and efficient in terms of storage space;
More information about TINs:
http://www.ian-ko.com/resources/triangulated_irregular_network.htm
Object Data Model

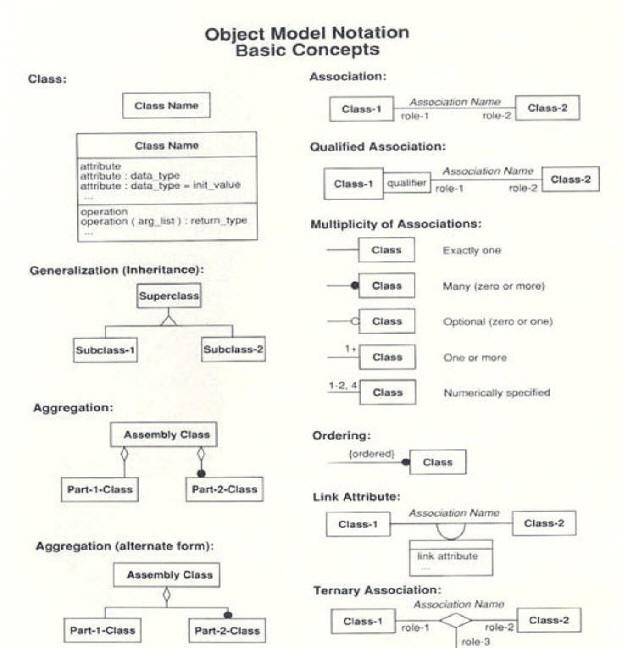
Images from the Book: Object-Oriented
Modeling and Design
by
James R Rumbaugh (Author),
Michael R. Blaha (Author),
William Lorensen (Author),
Frederick Eddy (Author),
William Premerlani (Author)
http://www.amazon.com/Object-Oriented-Modeling-Design-James-Rumbaugh/dp/0136298419
More resource:
http://java.sun.com/docs/books/tutorial/java/concepts/object.html
Youtube Video: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NtfJxA1J3h8
UML: Unified Modeling Language.
Discussion:
Give ONE examples of objects and their attributes.
What are the advantages of object model?
What is a “class” and what is a “rule”?
(Attribute rules, connectivity rules, relationship rules and geographic rules)
Object-Oriented GIS data model ? (Not really. Most of current GIS databases are still [Relational Database].
Hybrid GIS Data Model (Relational + OO)
Unit-4 In-Class Discussion Questions:
1. Please find ONE commercial-based software package (Not limited for GIS, the software could be any kinds) and ONE open source software package (with their URLs -- Web address) and discuss the advantages and disadvantages between the two software.
2. Please create and define THREE "related" Data Objects by following the rules of Object-Oriented Modeling and explain the three Objects' attributes, behaviors, and their relationships. (All three objects must be related to each other). Draw a diagram of the three objects by following the [Object Model Notation].
This web site is hosted on MAP.SDSU.EDU
and Geography Department.
|
|