
GEOG 581: Cartography Design

![]()
![]()
Cartographic Design and Map Elements
![]()
Announcement: Change of class schedule in November..
|
14 |
Nov 30 (Tuesday) (12:30). |
Visual Thinking and Visualization |
MacEachren Ch.8,9,10 |
Free Lab hour.. (No lab) |
![]()
HOW to design a "nice" map?
HOW to design a "useful" map?
http://www.telegeography.com/products/map_internet/index.php
Let's review some examples of the ESRI Map Books (2000-2004).
http://www.esri.com/mapmuseum/
Read Chapter 11, 12 (Slocum).
![]()
Most common map elements:
"Proper choices and implementation of map elements is governed in large part by the purpose of the map and its intended audience (the map users)." p. 201. (Slocum et al.).
1. Frame line and neat line: A frame line encloses all other map elements. .... The neat line is used to crop the mapped area.
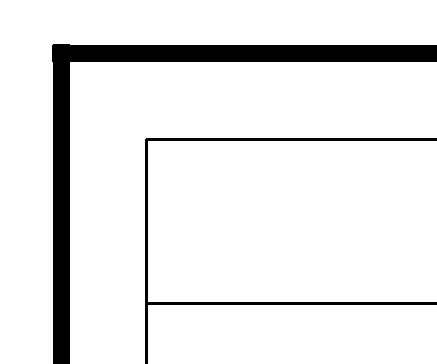
2. Mapped area: is the region of Earth being represented. (? Virtual reality map?)...
combine thematic symbols and base information.
Examples: http://map.sdsu.edu/website/fire2003eNEW/viewer.htm
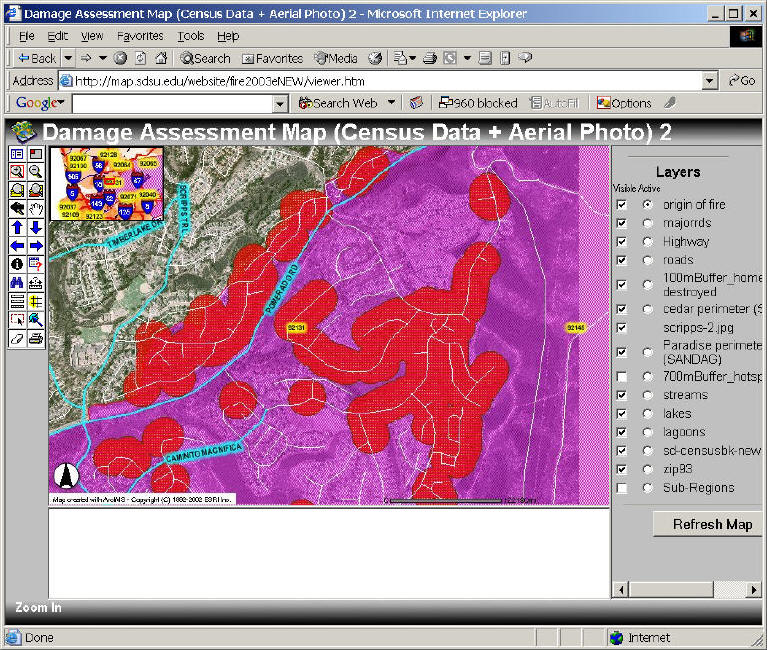
3. Inset: An inset is a smaller map included within the context of a larger map.
(see the previous ArcIMS example).
4. Title and subtitle
5. Legend: The legend is the map element that defines all of thematic symbols on a map. (a well-designed legend is self-explanatory and does not need to be identified with "legend" or "Key" labels., p. 206). The legend should be large enough to allow the map user to employ it easily, but should not be so large as to occupy vast areas of space, or challenge thematic symbols in the mapped area. p. 207).
Different ways to group legends: by points, lines, polygons, by the nature of data (human vs. physical..), or by thematic map vs. basemap.
6. Data Source
7. Scale (ArcMap: Scale Bar and Scale Text)
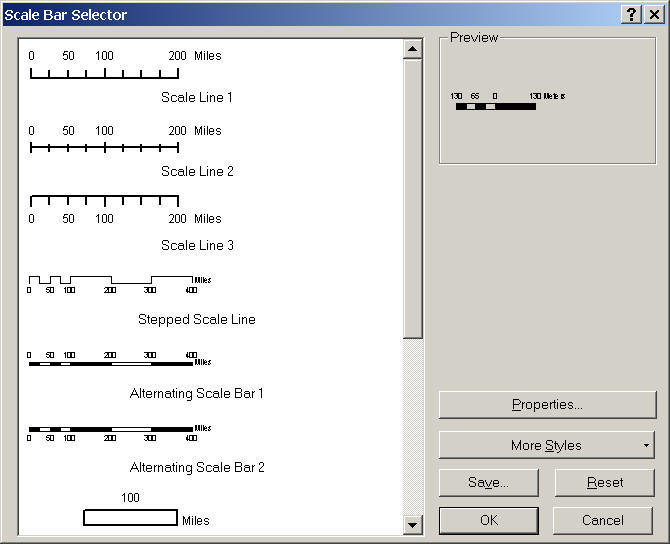
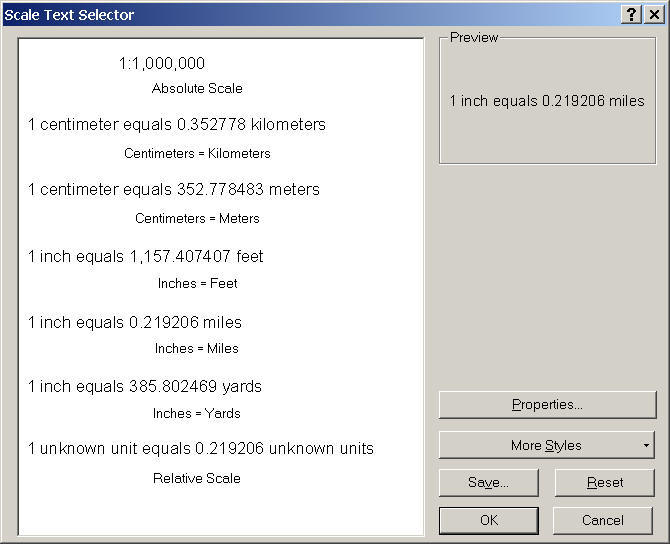
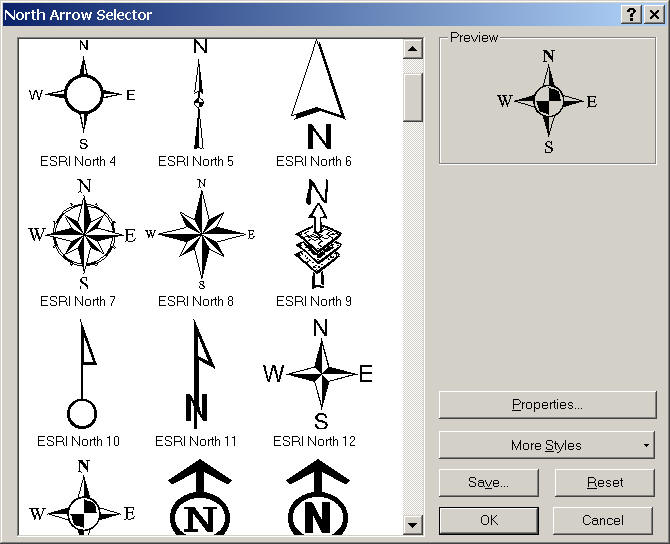
8. Orientation: (North arrow) or (Graticule -- grid lines)
![]()
TYPOGRAPHY
Type, or text, refers to the words that appear on maps. Typography is the art or process of specifying, arranging, and designing type. (p.212).
General typographic guidelines: (six rules).
Specific typographic guidelines: all features, point, linear, and areal features.
Automated Type Placement:
| ArcMap labeling engine (Maplex extension) | |
| Expert Systems (knowledge rules). |
![]()
The Map Design Process
(page. 220).
1. Determine how the map will be reproduced.
2. Select a scale and map projection that is appropriate for the map's theme.
3. Determine the most appropriate methods for data symbolization and classification.
4. Select which map elements to employ, and decide how each will be implemented.
5. Establish a ranking of symbols and map elements according to their relative importance. (This ranking is referred to as an intellectual hierarchy).
6. Create one or more sketch map or a thumbnail sketch.
7. Construct the map in your chosen software application. Print rough drafts first... then refine the map design.
8. If possible, allow members of the intended audience to evaluate the map's effectiveness.
(You will use this process for today's lab exercises and the next week. Read more information from Slocum's textbook from page 220-227 about Visual Hierarchy, Figure-Ground, and Balance.)
Visual Hierarchy: refers to the graphical representation of the intellectual hierarchy (map elements were ranked according to their relative importance).
Figure-Ground refers to methods of accentuating one object over another, based on the perception that one object stands in front of another and appears to be closer to the map user.
Balance refers to the organization of map elements and empty space, resulting in visual harmony and equilibrium.
![]()
Session TWO
![]()
Mid-term Exam Question Review
![]()
Map Reproduction:
Printing the Digital Maps:
Use Application software (ArcMap, Freehand, Imagine) --> Set up Printer Driver (PCL or PS)--> Convert to Raster Image Processor (RIP) --> Printing
Laser printing:
|
Monochromatic laser printers (letter size: 8.5" x 11"), http://computer.howstuffworks.com/laser-printer1.htm | |
|
Color laser printers. http://www.laser-printer-reviews.org/ |
Ink-Jet Printing: http://computer.howstuffworks.com/inkjet-printer.htm (selecting right printers for you... cable connections, printer's memory, printing resolution (DPI)...)
Other printing methods: Thermal-wax transfer printers ( http://whatis.techtarget.com/definition/0,,sid9_gci214446,00.htm ) , dye-sublimation printers (photo printer) http://www.shortcourses.com/how/printers/photoprinters.htm

File Format for Printing: EPS (Encapsulated PostScript), PDF (Portable Document Format)
Balance between printing speed and quality.
NON-print reproduction and dissemination: Web-based mapping / TV mapping / Computer mapping
![]()
Please use on-line forum to answer the following questions (LAST WEEK)
|
Write a paragraph about the purpose of your campus map (it could be a map for a new student orientation, or a map for facilitate management workers, or a map for a campus police). Give a specific description of your campus map and identify their major "functions". | |
|
Now, let's use a cognitive science aspect to analyze your campus. Write a discussion about How your campus map works? (from an information-processing view. (Using David Marr's four stage of vision). For example, when a police saw this campus map --> stage 1...--> stage 2:....--> stage 3:..... --> stage 4:...... (Describe more details as possible). | |
|
Explain what is the "figure" in your campus map? What is the "background" in the map? What kinds of mapping techniques or cartographic variables you applied in the design to make figure/ground effects in your campus map? Do you satisfy the result? WHY or WHY not? | |
|
What is "reference scale" in ArcMap setting? Did you use it in your campus map? WHY or WHY not? |
![]()
Web-powered by: MAP.SDSU.EDU