GEO 583 Internet Mapping and Distributed GIServices
![]()
UNIT ONE (Session I ):
![]()
INTRODUCTION
Instructor: Dr. Ming-Hsiang Tsou
What will you be learning in this class:
| Theories and technologies behind the Internet mapping facilities and Web GIS. | |
| Hands-on skills for Web-authoring and Internet Map Servers. | |
| The design principles of on-line mapping and Multimedia Cartography. |
NEW items: Making Video for Introducing Your Final Group Project
DEFINITION
What is "Internet mapping"?
What are the differences among "Internet mapping, on-line mapping, Web-based Mapping, on-line GIS, Internet GIS, or Web GIS"?
WHY "Internet mapping"?
Disaster Responses and Rescue Efforts.
Earthquake at Haiti
(Image source: http://www.redorbit.com/news/space/1809509/first_satellite_map_of_devastated_haiti/index.html )
(Click image to open the original size)
Geospatial Data/Mapping Web Portal for Earthquake: Haiti
http://cegrp.cga.harvard.edu/content/haiti-earthquake-data
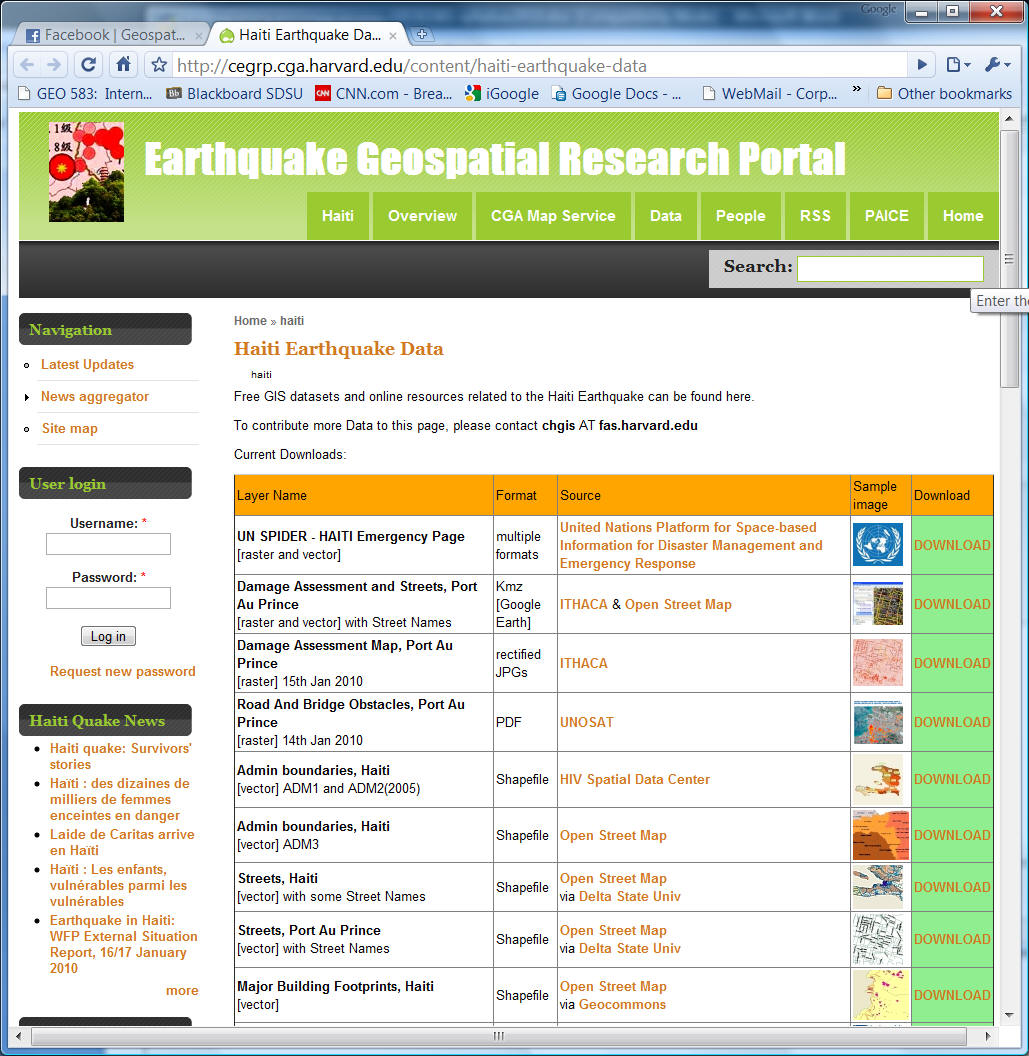
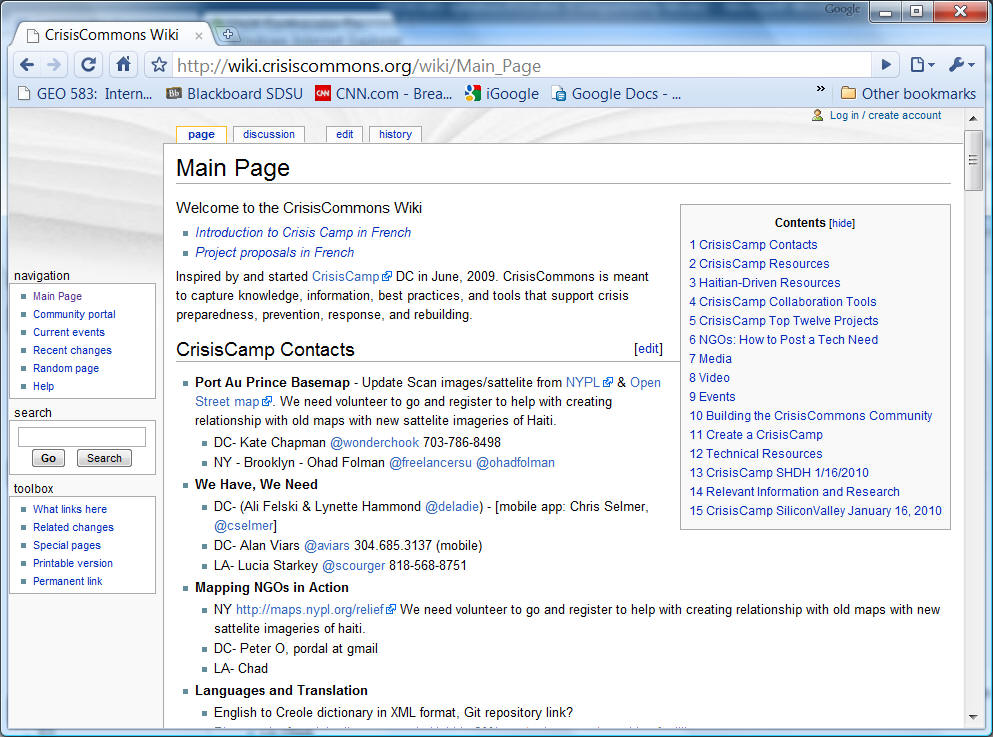
CrisisCamp (example of Volunteered Geographic Information).
http://wiki.crisiscommons.org/wiki/Main_Page
http://dgl.us.neolane.net/res/img/47a0e8459ac150960575ce4ef006bf3d.kml (KML link)
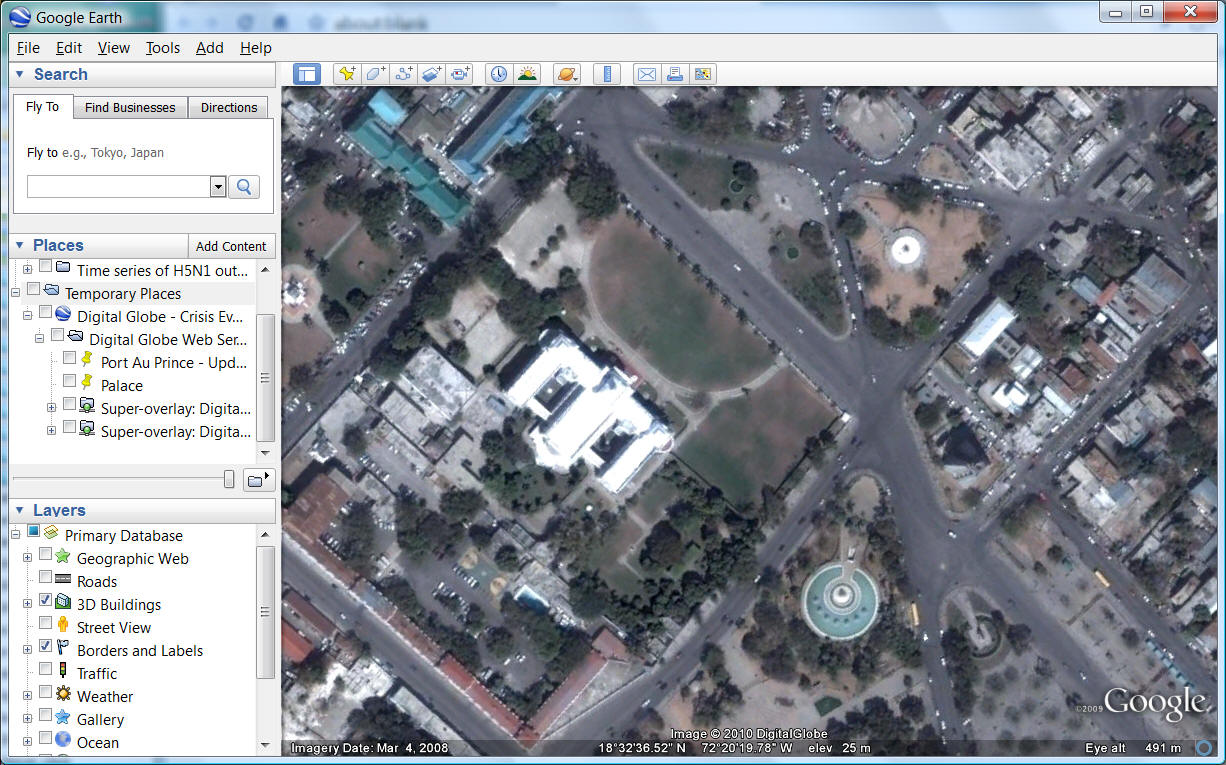
Before the Earthquake (Palace)
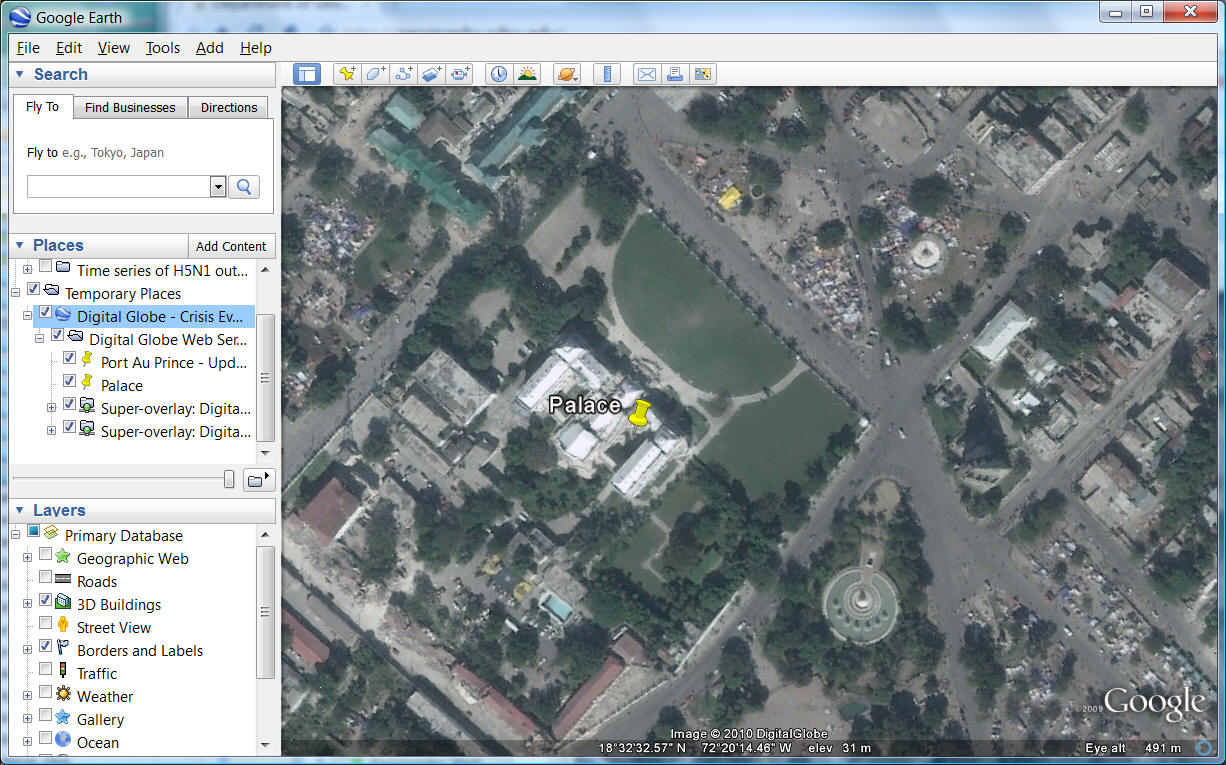
After the Earthquake (Palace)
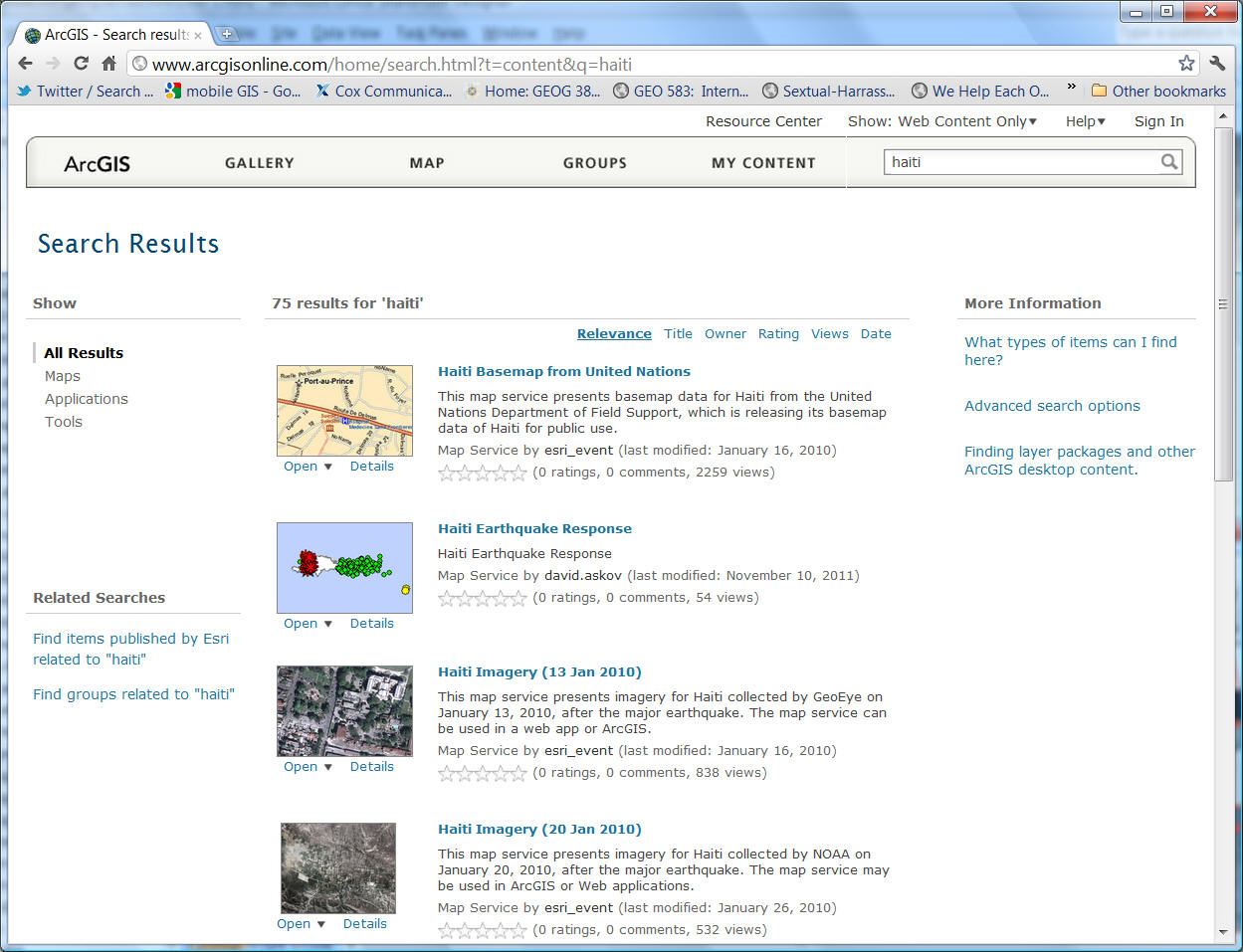
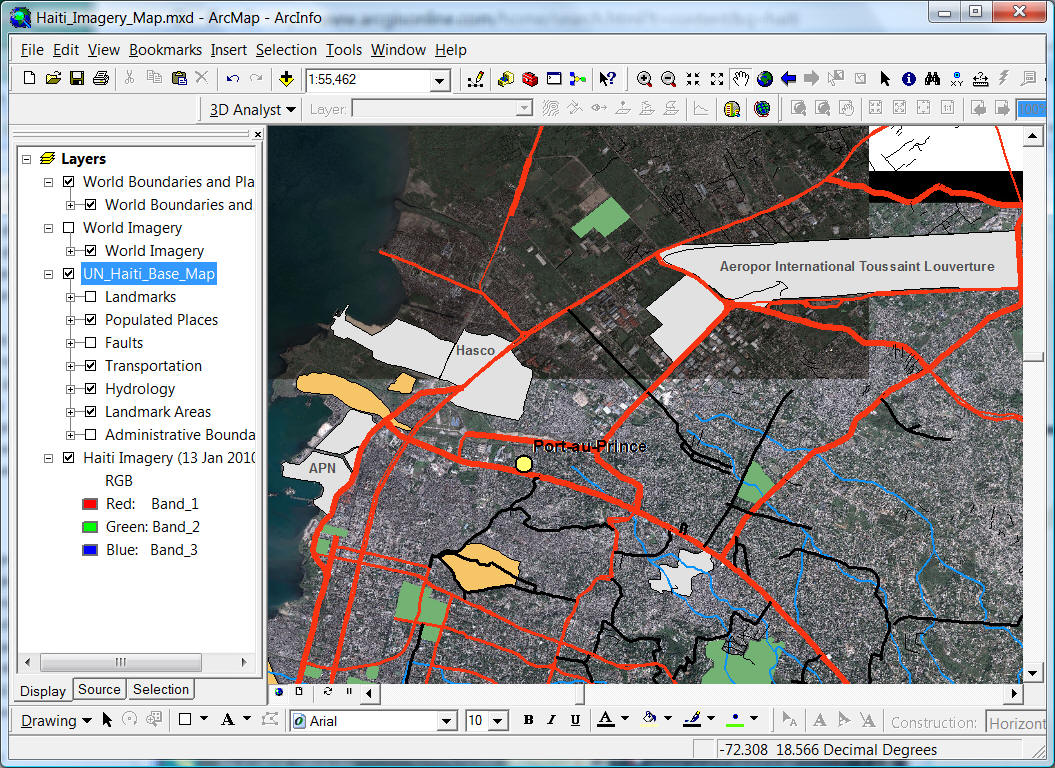
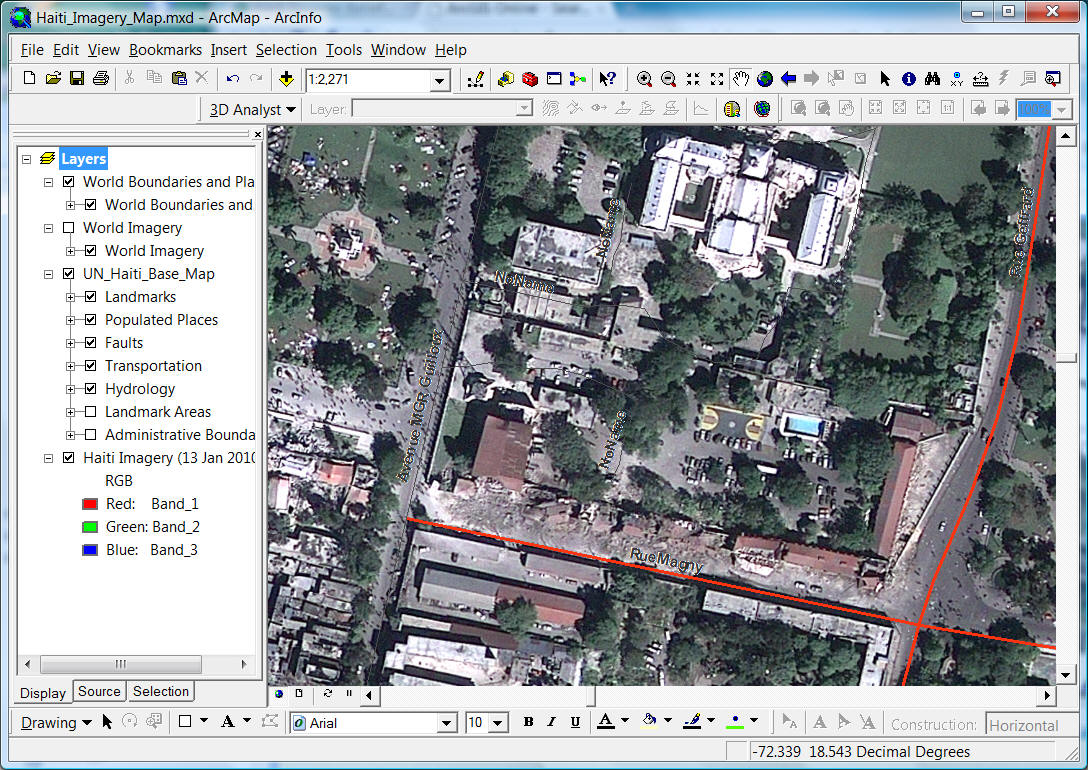
ESRI ArcGIS on-line
http://www.arcgisonline.com/home/search.html?t=content&q=haiti
![]()
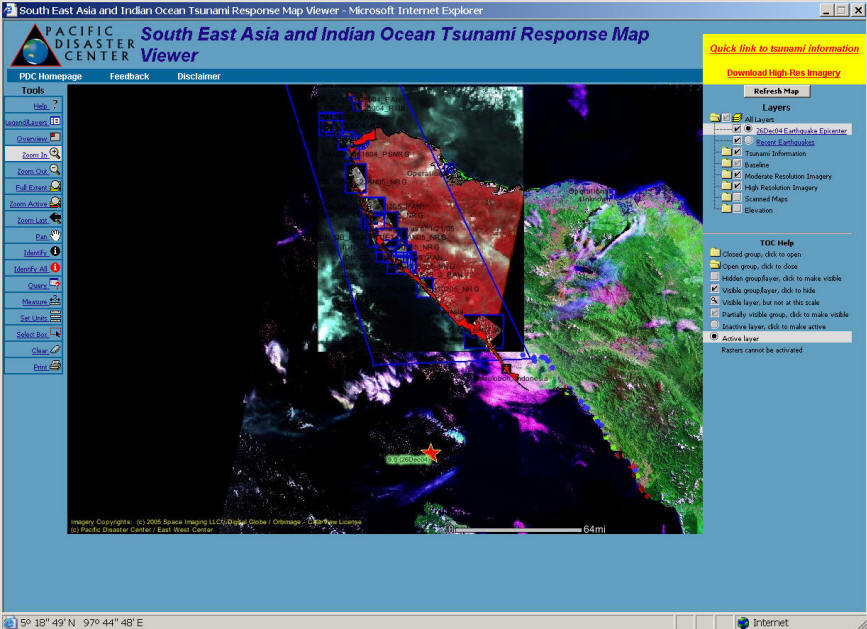
Real-time GIServices can provide an integrated framework for connecting various geospatial technologies including Global Positioning Systems (GPS), remote sensing images, spatial analysis functions, environmental monitoring sensors, Web-based mapping, and wireless communication.
The Pacific Disaster Center http://www.pdc.org/
![]()
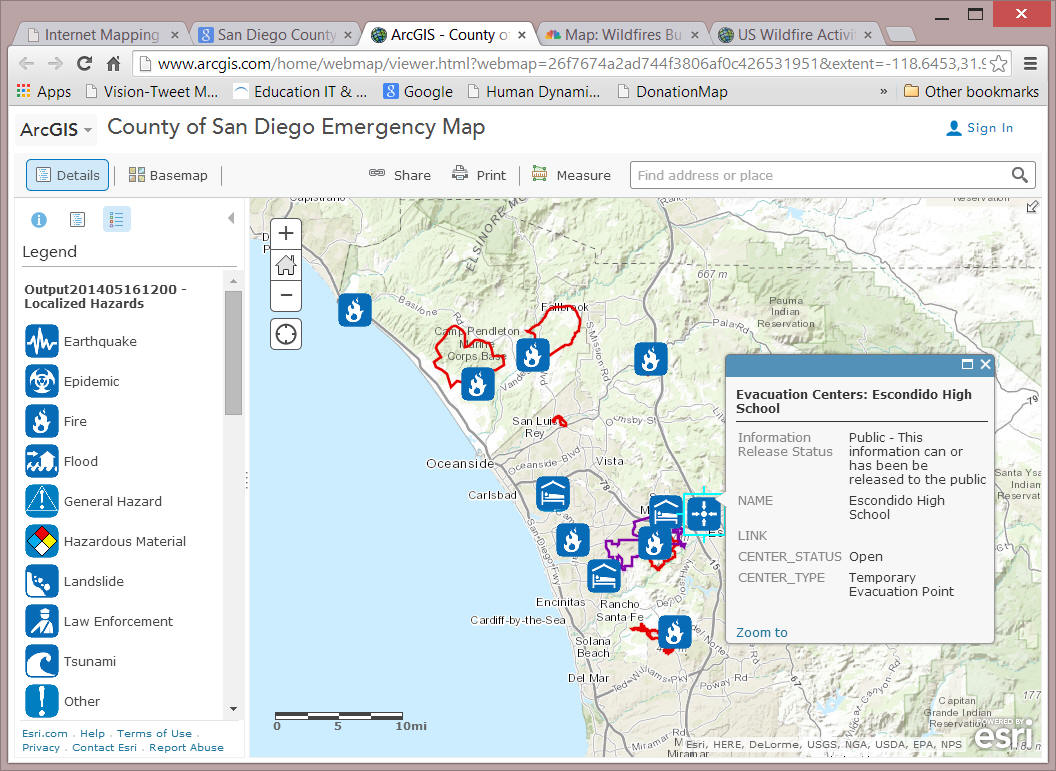
SAN DIEGO SCENARIO ( HTTP://map.sdsu.edu )
Wildfire 2003
Two wildfires (Cedar and Paradise) savaged San Diego County during the week of October 26. The wildfires kill 16 people and burned down 2427 homes and businesses (data source: www.signonsandiego.com ). These fires caused the worst damages in the history of San Diego and California. This web site (http://map.sdsu.edu) was created immediately on October 27 (Monday morning) to provide web mapping services for helping our local community. This site is updated daily and provides maps of the San Diego wildfires with various live ArcIMS web mapping services, static maps, and research articles. Most maps on this site have been created by the faculty, staff, and students in the Department of Geography, San Diego State University.
Wildfire 2007 HTTP://map.sdsu.edu
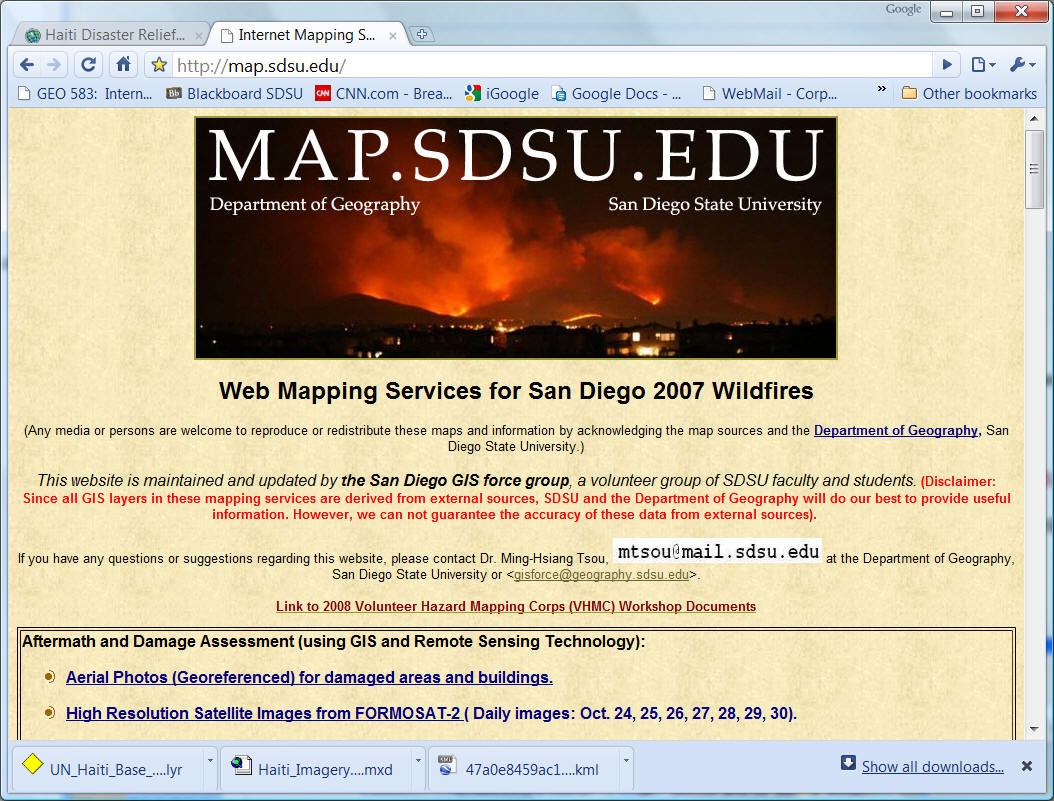
San Diego Wildfire 2014
The advantages of Internet Mapping:
|
Real time information | |
|
Easy to update | |
|
Multimedia presentation | |
|
Easy to access (no need for GIS software) | |
|
...... |
![]()
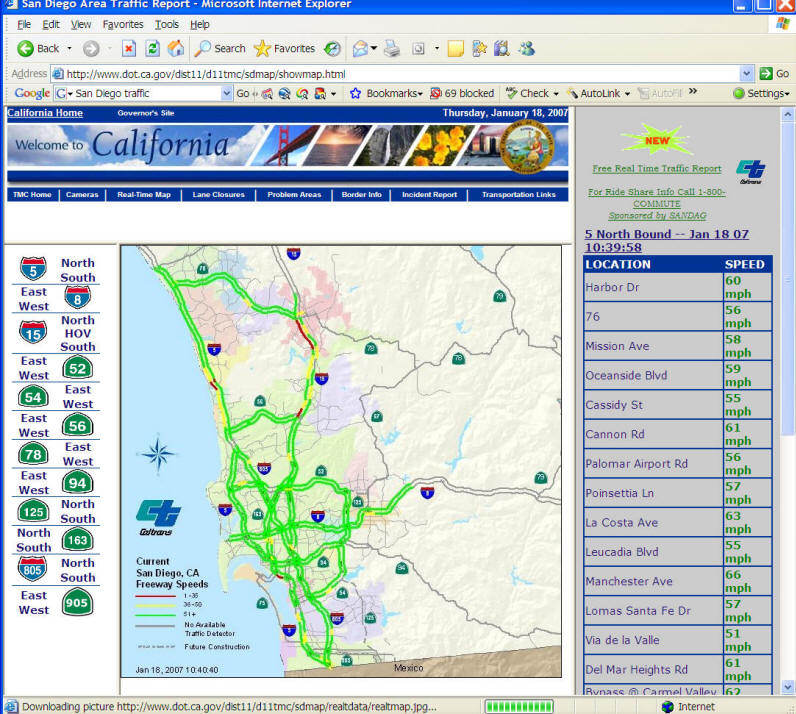
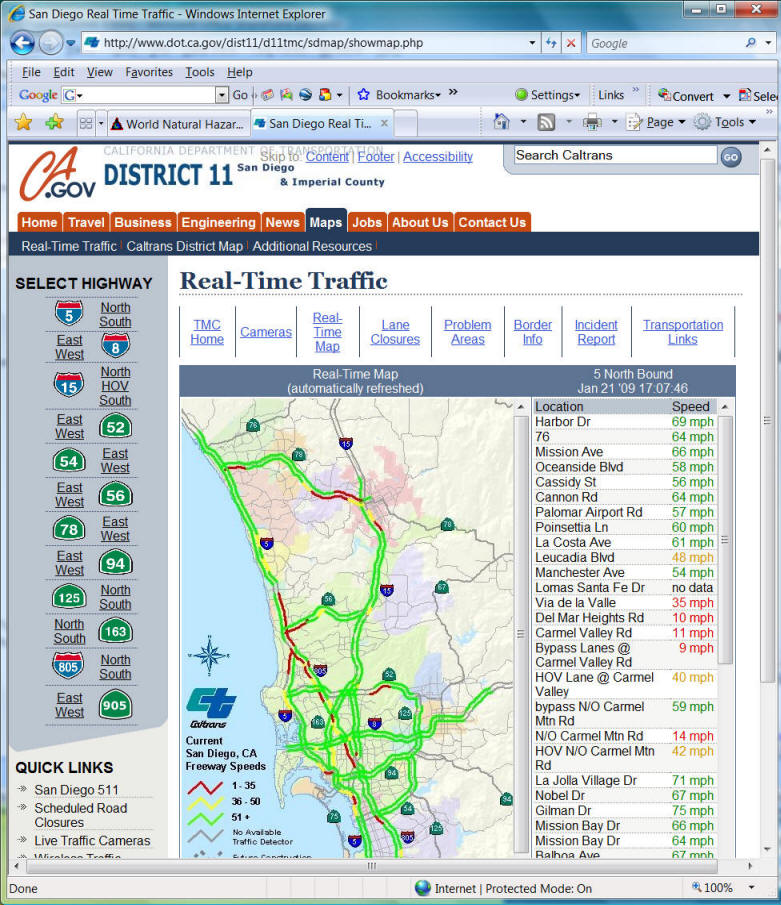
Real Time Update
What is "Real-time Update"? Every second? Every hour? Every day? Every week?
Different applications and contexts will have different requirement of real-time information.
http://www.dot.ca.gov/dist11/d11tmc/sdmap/showmap.html
2007
2009
![]()
Dynamic Presentation
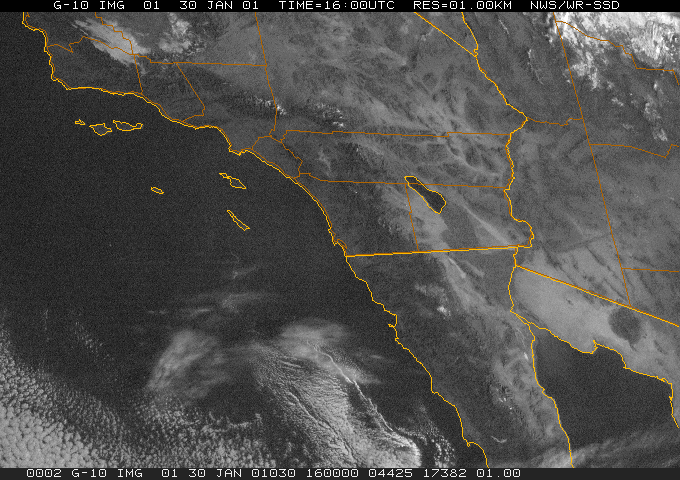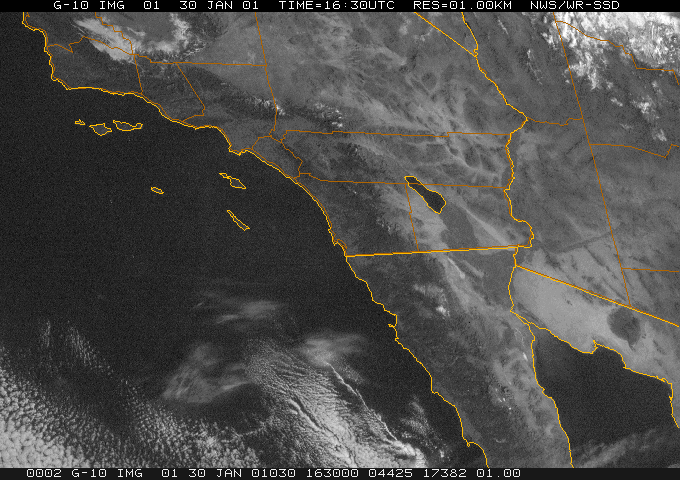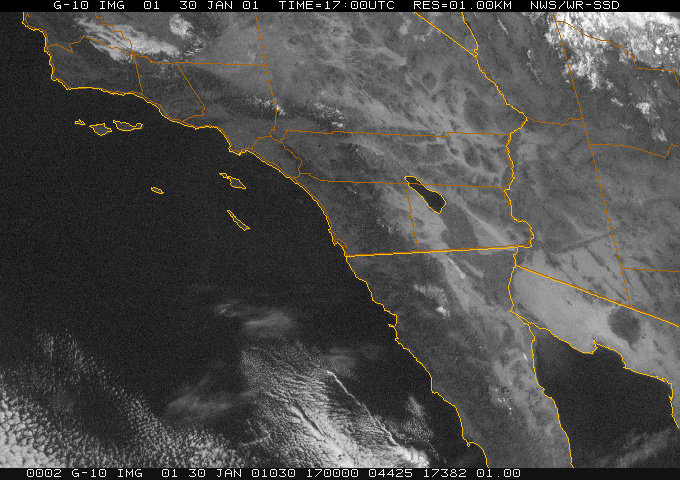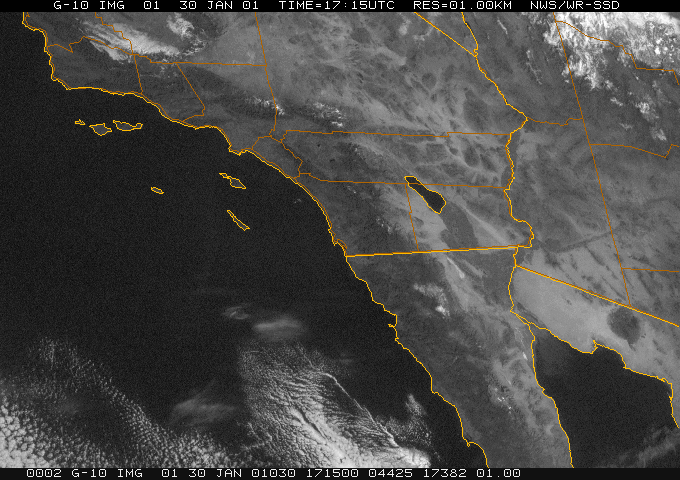
Data source: NOAA National Weather Service -- San Diego
Wireless Mobile GIS
Pocket PC (2003)
Google's G1 Phone (2007) (in T-Mobile)
(Android platform -- open operating system. Free development framework).
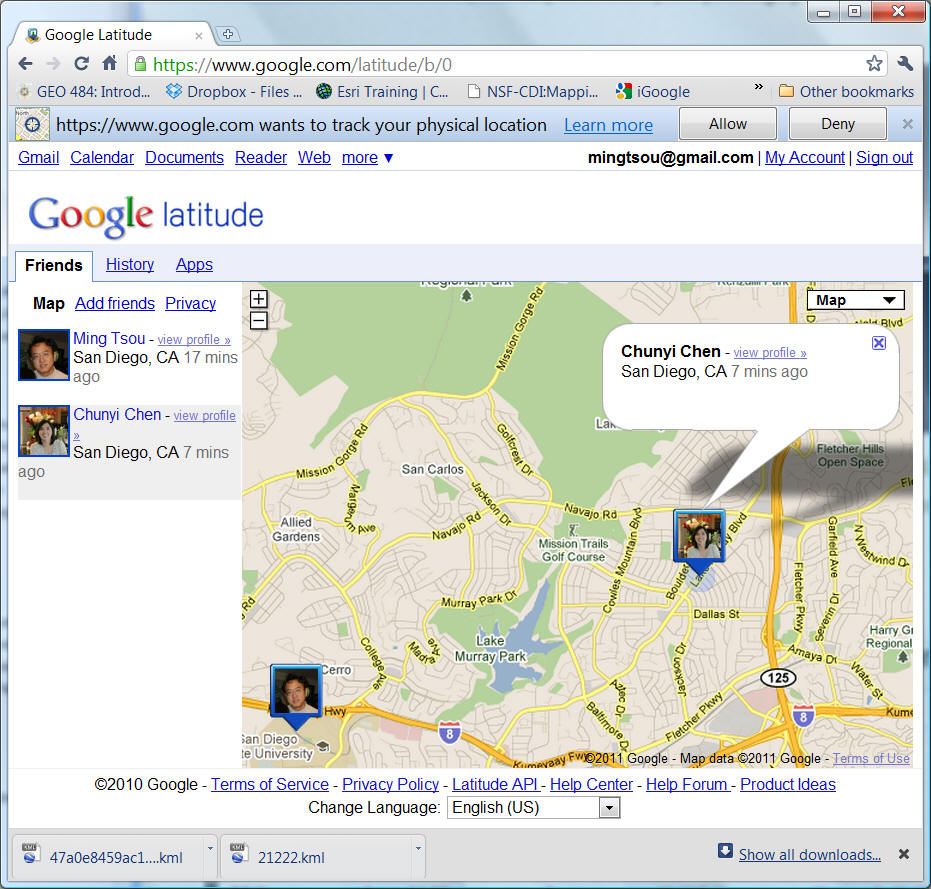
Google Latitude https://www.google.com/latitude
(Apps on Smart phones)
| What is "Distributed GIServices"? |
| What are the differences between "GISystems" and "GIServices"? |
On-line Forum Discussion.
Code of Conduct
Please fill out the questionnaires and return to me.
We will use Blackboard email function for this class. Make sure you update the current email addresses in Blackboard.
First Reading Assignment:
Butler, Declan (2006). The web-wide world. Nature, 439(16). February 2006, pp. 776-778. (Blackboard --> "Course documents").
![]()
Unit ONE (Session II):
![]()
Technology Demo (Please select ONE week for your Demo Day).
Use Blackboard to Upload your Demo Site and Introduction Information.
![]()
The History of the Internet
![]()
Network technology evolved from
local area networks (LAN) to wide area networks (WAN) to the Internet (Inter-networking) (Sloman, 1994).
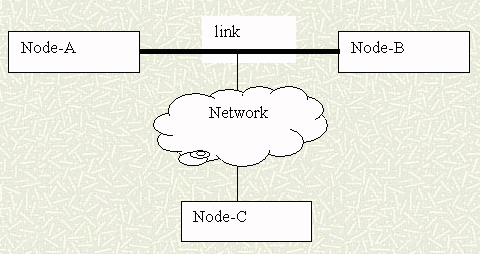
LAN Example: Department of Geography, SAL lab (Ethernet, Wireless ).
WAN Example: San Diego County Area (ADSL Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line, Cable Modem).
similar to Metropolitan area network (MAN)
Internet: Inter-networking (connecting different kinds of networks together) ( T-Carrier- T1, T2, T3, Optic Fiber).
Pink color = physical network types and media (related to bandwidth).
Brown color = network topology and connectivity (related to service area).
More explanations in
The icons of network are usually represented in "clouds" in network graphs. Recently, the term, "cloud computing", has been adopted for network-based computing technology.
Cloud computing is Internet ("cloud") based development and use of computer technology ("computing")[1][2][3]. It is a business information management style of computing in which typically real-time scalable[4] resources are provided “as a service”[5] over the Internet[6] to users who need not have knowledge of, expertise in, or control over the technology infrastructure ("in the cloud") that supports them[7].
It is a general concept that incorporates software as a service (SaaS), Web 2.0 and other recent, well-known technology trends, in which the common theme is reliance on the Internet for satisfying the computing needs of the users. An often-quoted example is Google Apps, which provides common business applications online that are accessed from a web browser, while the software and data are stored on Google servers.
The cloud is a metaphor for the Internet, based on how it is depicted in computer network diagrams, and is an abstraction for the complex infrastructure it conceals.[8]
![]()
ARPANET and TCP/IP
The progenitor of the modern Internet was a network called ARPANET (http://www.cybergeography.org/atlas/historical.html
), set up in the 1970s by the U.S. Defense Department, developing a self-adjustable, decentralized networking system. The original goal of the ARPANET project was to provide a reliable telecommunications network which would persist after nuclear war. In 1983, the ARPANET project adopted the Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) as the standardized protocol for communications across interconnected networks, between computers with diverse hardware architectures, and between various operating systems. The dramatic success of the Internet and the popular adoption of TCP/IP pushed network development into a new age. Along with the rapid development of the Internet, many applications and programs have been developed, such as Newsgroup, Gopher, Bulletin Board System (BBS), Telnet, etc. The following figure illustrates the screen shot of the Gopher information Client via the Telnet application, which was one of the most popular Internet applications before the World Wild Wed.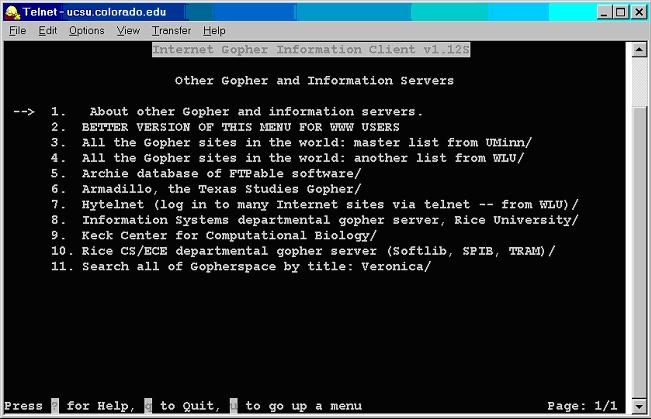
The Gopher information client on a Telnet application window.
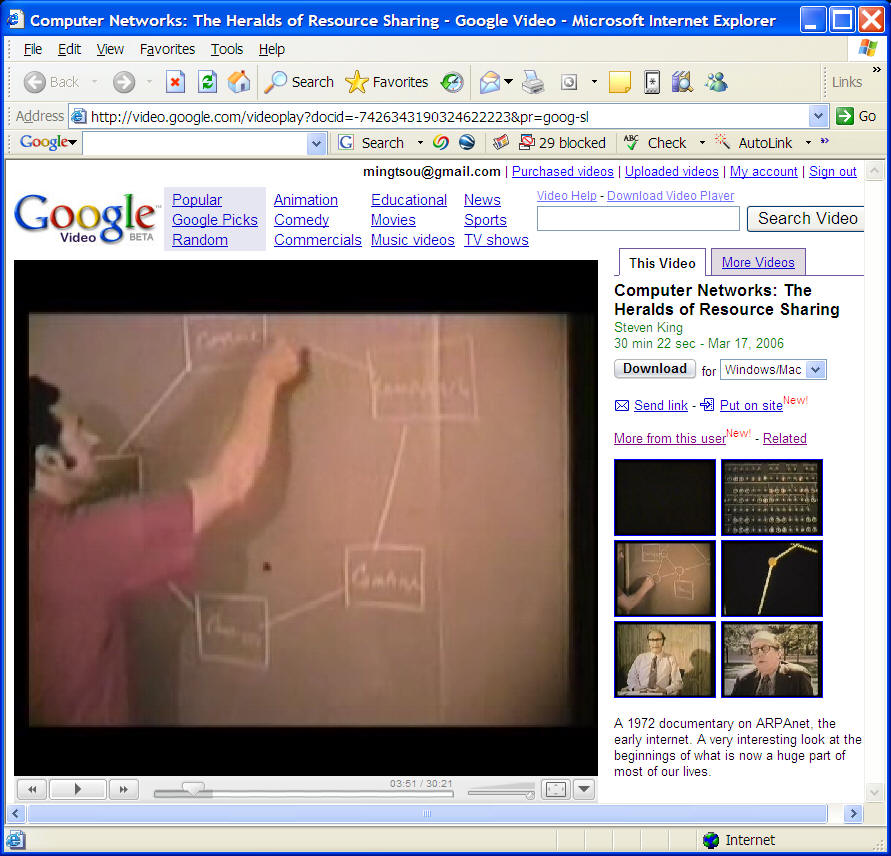
Click to watch: http://archive.org/details/ComputerNetworks_TheHeraldsOfResourceSharing
Computer Networks: The Heralds of Resource Sharing
Description: A 1972 documentary on ARPAnet, the early internet. A very
interesting look at the beginnings of what is now a huge part of most of our
lives.
(Show the first 8 minutes video).
Another milestone in the history of the Internet is the NSFNET backbone, which replace the ARPANET and provided a preliminary global network architecture for today's information superhighway. In 1985, the National Science Foundation (NSF) added five supercomputer centers (NSFNET) to the Internet and create the NSFNET backbone. Later on, NSF began an effort to privatize the backbone functions and the NSFNET backbone was replaced by a commercial Internet backbone. At the same time, the NSF implemented a new backbone architecture called very high-speed Backbone Network Service (vBNS), which serves as a testing ground for the next generation of Internet technologies.
Link: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/National_Science_Foundation_Network
The World Wide Web (the Web)
is currently one of the fastest growing applications on the Internet for the public to publish and retrieve information. The original idea of the Web was to serve as a pool of human knowledge, which could allow researchers in remote sites to exchange ideas on a common project (Berners-Lee, et al., 1994). The Web adopts a standardized communication protocol, HyperText Transfer Protocol (HTTP), for disseminating multimedia documents on the Internet. The HyperText Transfer Protocol was developed by the European Laboratory for Particle Physics in Geneva (CERN) in 1990. Later the protocol was popularized with the appearance of Mosaic in 1993, a multimedia browser created at the National Center for Supercomputing Applications (NCSA). The Web provides an integrated method to distribute all types of data across all different types of computers in a unified format, called HyperText Markup Language (HTML). The main reason for the popular growth of the Web is its powerful capability of presenting multimedia documents on the Internet which can include texts, sounds, pictures, animation, etc. Other Internet applications, such as Newsgroup, BBS, and Gopher, only provide text-based information.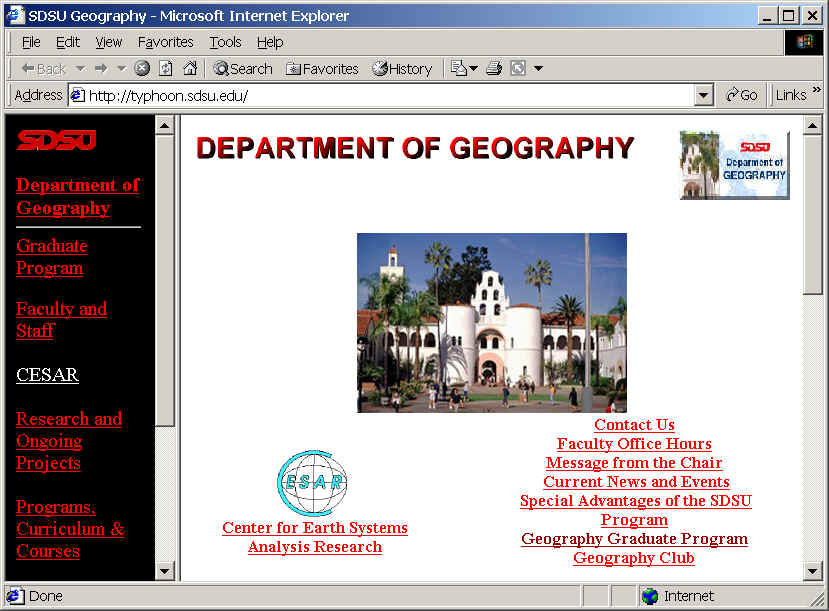
An Example of World Wide Wed Home Page (Year 2000), Department of Geography, San Diego State University.


The Web uses hypertext and multimedia techniques to make its content accessible to anyone. People can easily generate home pages by adding pictures, sounds, and hyperlinks in HTML format and create attractive contents on the specific topics. Since the powerful communication and popular use of the Web, many GIS researchers have launched some pioneering research and are developing applications on the Web.
![]()
On-line Discussion Forum (Blackboard) http://blackboard.sdsu.edu
Additional Reading: (PDF file --> //geog583/data/reading)
Student Group Project Examples.
SanDAG Example (DATA sources)
Microsoft SharePointDesigner (Frontpage) Intro.
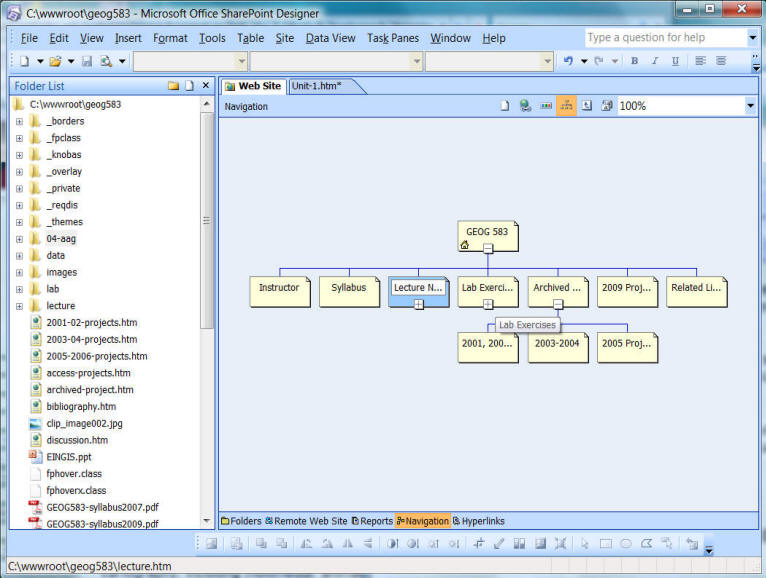
![]()
User accounts and passwords
Assignment: (0 points for the LAB Grade - first warming exercise)
Use the On-line forum (Blackboard) to answer the following questions: (Suggestions: You should write down your answer in the Word or any text editor and then copy/paste to the Forum in case of losing computer network connection or Web server problems )
1. What are the differences between the Internet and World Wide Web?
2. What are the differences between "information systems" and "information services"?
3. Use different search engine (such as www.google.com, www.yahoo.com , or your preferred search engine) to search for web mapping applications related to Disease Outbreaks, Climate Change, or Flooding. Write a short paragraph (150-200 words) to describe the web map, the URL, and explain whether you like this mapping services or not and WHY.
![]()